Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMCFE9I)
| Drug Name |
Valproate
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
99-66-1; Dipropylacetic acid; Depakine; Depakene; 2-Propylvaleric acid; Ergenyl; Di-n-propylacetic acid; Mylproin; Pentanoic acid, 2-propyl-; 4-Heptanecarboxylic acid; Propylvaleric acid; n-Dipropylacetic acid; Myproic Acid; Di-n-propylessigsaure; n-DPA; Dipropylacetate; Convulex; Depakin; Vupral; Acido valproico; Acide valproique; Acidum valproicum; Stavzor; Avugane; Baceca; Kyselina 2-propylvalerova; 2-n-Propyl-n-valeric acid; Acetic acid, dipropyl-; Abbott 44090; Valproinsaeure; Savicol; Convulsofin; Deproic; VPA; Depakin chrono; Dipropyl Acetate; Med Valproic; Valproic acid USP; Valproic acid USP24; Acide valproique [INN-French]; Acido valproico [INN-Spanish]; Acidum valproicum [INN-Latin]; Alti-Valproic; Depakote (TM); Dom-Valproic; G2M-777; Kyselina 2-propylvalerova [Czech]; N-DPA; N-Dipropylacetic acid; Novo-Valproic; Nu-Valproic; PMS-Valproic Acid; Penta-Valproic; Valproic acid (USP); Di-n-propylessigsaeure; Di-n-propylessigsaure [German]; Valproic acid [USAN:INN:BAN]; Valproic Acid, SodiumSalt (2:1); 2 PP (base)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Neurology Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
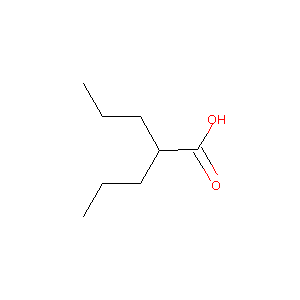 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 144.21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Valproate
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Valproate (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7009). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Challenges and new opportunities in the investigation of new drug therapies to treat frontotemporal dementia. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008 Nov;12(11):1367-76. | ||||
| 3 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 4 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 5 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | Transcription-independent heritability of induced histone modifications in the mouse preimplantation embryo. PLoS One. 2009 Jun 30;4(6):e6086. | ||||
| 8 | Monocarboxylate Transporters in Drug Disposition: Role in the Toxicokinetics and Toxicodynamics of the Drug of Abuse GHB. | ||||
| 9 | Pharmacogenetics of membrane transporters: an update on current approaches. Mol Biotechnol. 2010 Feb;44(2):152-67. | ||||
| 10 | A mechanistic approach to antiepileptic drug interactions. Ann Pharmacother. 1998 May;32(5):554-63. | ||||
| 11 | Effect of aging on glucuronidation of valproic acid in human liver microsomes and the role of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase UGT1A4, UGT1A8, and UGT1A10. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009 Jan;37(1):229-36. | ||||
| 12 | Psychotropic drug interactions with valproate. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2005 Mar-Apr;28(2):96-101. | ||||
| 13 | Substrates, inducers, inhibitors and structure-activity relationships of human Cytochrome P450 2C9 and implications in drug development. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(27):3480-675. | ||||
| 14 | Insights into CYP2B6-mediated drug-drug interactions. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2016 Sep;6(5):413-425. | ||||
| 15 | Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interaction of lorazepam and valproic acid in relation to UGT2B7 genetic polymorphism in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008 Apr;83(4):595-600. | ||||
| 16 | UDP glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A6 pharmacogenetics: II. Functional impact of the three most common nonsynonymous UGT1A6 polymorphisms (S7A, T181A, and R184S). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Jun;313(3):1340-6. | ||||
| 17 | The neuroprotective action of the mood stabilizing drugs lithium chloride and sodium valproate is mediated through the up-regulation of the homeodomain protein Six1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009 Feb 15;235(1):124-34. | ||||
| 18 | Valproic acid augments vitamin D receptor-mediated induction of CYP24 by vitamin D3: a possible cause of valproic acid-induced osteomalacia?. Toxicol Lett. 2011 Feb 5;200(3):146-53. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.11.008. Epub 2010 Nov 27. | ||||
| 19 | Human embryonic stem cell-derived test systems for developmental neurotoxicity: a transcriptomics approach. Arch Toxicol. 2013 Jan;87(1):123-43. | ||||
| 20 | Integrative omics data analyses of repeated dose toxicity of valproic acid in vitro reveal new mechanisms of steatosis induction. Toxicology. 2018 Jan 15;393:160-170. | ||||
| 21 | Gene Expression Regulation and Pathway Analysis After Valproic Acid and Carbamazepine Exposure in a Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Based Neurodevelopmental Toxicity Assay. Toxicol Sci. 2015 Aug;146(2):311-20. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv094. Epub 2015 May 15. | ||||
| 22 | In vitro assessment of drug-induced liver steatosis based on human dermal stem cell-derived hepatic cells. Arch Toxicol. 2016 Mar;90(3):677-89. doi: 10.1007/s00204-015-1483-z. Epub 2015 Feb 26. | ||||
| 23 | Bourgeois BF "Pharmacologic interactions between valproate and other drugs." Am J Med 84 (1988): 29-33. [PMID: 3146222] | ||||
| 24 | Henriksen O, Johannessen SI "Clinical and pharmacokinetic observations on sodium valproate: a 5-year follow-up study in 100 children with epilepsy." Acta Neurol Scand 65 (1982): 504-23. [PMID: 6810648] | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Gabitril (tiagabine). Abbott Pharmaceutical, Abbott Park, IL. | ||||
| 26 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 27 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 28 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 30 | Karonen T, Filppula A, Laitila J, Niemi M, Neuvonen PJ, Backman JT "Gemfibrozil Markedly Increases the Plasma Concentrations of Montelukast: A Previously Unrecognized Role for CYP2C8 in the Metabolism of Montelukast." Clin Pharmacol Ther (2010):. [PMID: 20592724] | ||||
| 31 | Fu C, Katzman M, Goldbloom DS "Valproate/nortriptyline interaction." J Clin Psychopharmacol 14 (1994): 205-6. [PMID: 8027418] | ||||
| 32 | Anderson GD, Yau MK, Gidal BE, Harris SJ, Levy RH, Lai AA, Wolf KB, Wargin WA, Dren AT "Bidirectional interaction of valproate and lamotrigine in healthy subjects." Clin Pharmacol Ther 60 (1996): 145-56. [PMID: 8823232] | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Alinia (nitazoxanide). Romark Laboratories L.C., Tampa, FL. | ||||
| 35 | Belcastro V, Costa C, Striano P "Levetiracetam-associated hyponatremia." Seizure 17 (2008): 389-90. [PMID: 18584781] | ||||
| 36 | Guthrie SK, Stoysich AM, Bader G, Hilleman DE "Hypothesized interaction between valproic acid and warfarin." J Clin Psychopharmacol 15 (1995): 138-9. [PMID: 7782487] | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Stivarga (regorafenib). Bayer Pharmaceutical Inc, West Haven, CT. | ||||
| 38 | Warrington SJ, Ankier SI, Turner P "Evaluation of possible interactions between ethanol and trazodone or amitriptyline." Neuropsychobiology 15 (1986): 31-7. [PMID: 3725002] | ||||
| 39 | Tartara A, Galimberti CA, Manni R, et al "Differential effects of valproic acid and enzyme-inducing anticonvulsants on nimodipine pharmacokinetics in epileptic patients." Br J Clin Pharmacol 32 (1991): 335-40. [PMID: 1777370] | ||||
| 40 | Corrigan FM "Sodium valproate augmentation of fluoxetine or fluvoxamine effects." Biol Psychiatry 31 (1992): 1178-9. [PMID: 1525286] | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Alphagan (brimonidine ophthalmic). Allergan Inc, Irvine, CA. | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 43 | Lertora JJ, Rege AB, Greenspan DL, et al "Pharmacokinetic interaction between zidovudine and valproic acid in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus." Clin Pharmacol Ther 56 (1994): 272-8. [PMID: 7924122] | ||||
| 44 | Elsharkawy AM, Schwab U, McCarron B, et al. "Efavirenz induced acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation in a slow drug metaboliser." J Clin Virol 58 (2013): 331-3. [PMID: 23763943] | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Zurampic (lesinurad). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 49 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 51 | Product Information. Clolar (clofarabine). sanofi-aventis, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 53 | Product Information. Addyi (flibanserin). Sprout Pharmaceuticals, Raleigh, NC. | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Thalomid (thalidomide). Celgene Corporation, Warren, NJ. | ||||
| 55 | Bigham S, McGuigan C, MacDonald BK "Reduced absorption of lipophilic anti-epileptic medications when used concomitantly with the anti-obesity drug orlistat." Epilepsia 47 (2006): 2207. [PMID: 17201727] | ||||
| 56 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 57 | Hansen BS, Dam M, Brandt J, et al "Influence of dextropropoxyphene on steady state serum levels and protein binding of three anti-epileptic drugs in man." Acta Neurol Scand 61 (1980): 357-67. [PMID: 6998251] | ||||
| 58 | Abbott FS, Kassam J, Orr JM, Farrell K "The effect of aspirin on valproic acid metabolism." Clin Pharmacol Ther 40 (1986): 94-100. [PMID: 3087680] | ||||
| 59 | Dasgupta A, Volk A "Displacement of valproic acid and carbamazepine from protein binding in normal and uremic sera by tolmetin, ibuprofen, and naproxen: presence of inhibitor in uremic serum that blocks valproic acid-naproxen interactions." Ther Drug Monit 18 (1996): 284-7. [PMID: 8738769] | ||||
| 60 | Sekar M, Mimpriss TJ "Buprenorphine, benzodiazepines and prolonged respiratory depression." Anaesthesia 42 (1987): 567-8. [PMID: 3592200] | ||||
| 61 | Lambertsen CJ, Wendel H, Longenhagen JB "The separate and combined respiratory effects of chlorpromazine and meperidine in normal men controlled at 46 mm Hg alveolar pCO2." J Pharmacol Exp Ther 131 (1961): 381-93. [PMID: 13758472] | ||||
| 62 | Product Information. Nexium (esomeprazole) Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 63 | Product Information. Zokinvy (lonafarnib). Eiger BioPharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA. | ||||
| 64 | Product Information. Celebrex (celecoxib). Searle, Chicago, IL. | ||||
| 65 | Baldassano CF, Ghaemi SN "Generalized edema with risperidone: divalproex sodium treatment." J Clin Psychiatry 57 (1996): 422. [PMID: 9746451] | ||||
| 66 | Dasgupta A, Jacques M "Reduced in vitro displacement of valproic acid from protein binding by salicylate in uremic sera compared with normal sera - role of uremic compounds." Am J Clin Pathol 101 (1994): 349-53. [PMID: 8135194] | ||||
| 67 | Product Information. Levitra (vardenafil). Bayer, West Haven, CT. | ||||
| 68 | Product Information. ReVia (naltrexone). DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 69 | Product Information. Zyrtec (cetirizine). Pfizer US Pharmaceuticals, New York, NY. | ||||
