Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM7BN0X)
| Drug Name |
Esomeprazole
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Esomeprazolum; Nexiam; Inexium paranova; Axagon (TN); Esomeprazole (INN); Esomeprazole [INN:BAN]; Esopral (TN); Inexium paranova (TN); Lucen (TN); Nexiam (TN); Nexium (TN); Sompraz (TN); Zoleri (TN); (S)-(-)-Omeprazole; (S)-Omeprazole; 5-Methoxy-2-((S)-((4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyridyl)methyl)sulfinyl)benzimidazole; 5-methoxy-2-{(S)-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfinyl}-1H-benzimidazole; 5-methoxy-2-{[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfinyl}-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazole
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiulcer Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
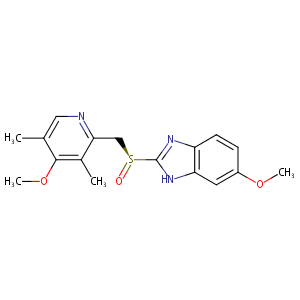 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 345.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Esomeprazole (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Esomeprazole FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5488). | ||||
| 3 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 4 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 5 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 6 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 7 | Predictive performance of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling of drugs extensively metabolized by major cytochrome P450s in children. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Jul;104(1):188-200. | ||||
| 8 | The effects of drugs with immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory activities on xenobiotics-metabolizing enzymes expression in primary human hepatocytes. Toxicol In Vitro. 2015 Aug;29(5):1088-99. | ||||
| 9 | Honig PK, Gillespie BK "Clinical significance of pharmacokinetic drug interactions with over-the-counter (OTC) drugs." Clin Pharmacokinet 35 (1998): 167-71. [PMID: 9784931] | ||||
| 10 | Humphries TJ "Clinical implications of drug interactions with the cytochrome P-450 enzyme system associated with omeprazole." Dig Dis Sci 36 (1991): 1665-9. [PMID: 1748033] | ||||
| 11 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 12 | FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration "FDA Drug Safety Communication: Low magnesium levels can be associated with long-term use of proton pump inhibitor drugs (PPIs).". | ||||
| 13 | Hedaya MA, El-Afify DR, El-Maghraby GM "The effect of ciprofloxacin and clarithromycin on sildenafil oral bioavailability in human volunteers." Biopharm Drug Dispos 27 (2006): 103-10. [PMID: 16372380] | ||||
| 14 | Alffenaar JW, van Assen S, van der Werf TS, Kosterink JG, Uges DR "Omeprazole significantly reduces posaconazole serum trough level." Clin Infect Dis 48 (2009): 839. [PMID: 19220151] | ||||
| 15 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 16 | Product Information. Spectracef (cefditoren). TAP Pharmaceuticals Inc, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 17 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Bosulif (bosutinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 19 | Bogman K, Peyer AK, Torok M, Kusters E, Drewe J "HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and P-glycoprotein modulation." Br J Pharmacol 132 (2001): 1183-92. [PMID: 11250868] | ||||
| 20 | Ahmad S "Omeprazole-warfarin interaction." South Med J 84 (1991): 674-5. [PMID: 2035104] | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Isturisa (osilodrostat). Recordati Rare Diseases Inc, Lebanon, NJ. | ||||
| 22 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Canadian Product Information.". | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 24 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Xcopri (cenobamate). SK Life Science, Inc., Paramus, NJ. | ||||
| 26 | Klotz U "The role of pharmacogenetics in the metabolism of antiepileptic drugs: pharmacokinetic and therapeutic implications." Clin Pharmacokinet 46 (2007): 271-9. [PMID: 17375979] | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Nexium (esomeprazole) Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 28 | Bottiger Y, Tybring G, Gotharson E, Bertilsson L "Inhibition of the sulfoxidation of omeprazole by ketoconazole in poor and extensive metabolizers of S-mephenytoin." Clin Pharmacol Ther 62 (1997): 384-91. [PMID: 9357389] | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Lexiva (fosamprenavir). GlaxoSmithKline, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Edurant (rilpivirine). Tibotec Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 32 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Isentress (raltegravir). Merck & Company Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 34 | Hutchison C, Geissler CA, Powell JJ, Bomford A "Proton pump inhibitors suppress absorption of dietary non-haem iron in hereditary haemochromatosis." Gut 56 (2007): 1291-5. [PMID: 17344278] | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Zykadia (ceritinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Copiktra (duvelisib). Verastem, Inc., Needham, MA. | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Calquence (acalabrutinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Addyi (flibanserin). Sprout Pharmaceuticals, Raleigh, NC. | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Tasigna (nilotinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Sprycel (dasatinib). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Effient (prasugrel). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 42 | Miner PB Jr, Fort JG, Zhang Y. Intragastric acidity and omeprazole exposure during dosing with either PA32540 (enteric-coated aspirin 325?mg + immediate-release omeprazole 40?mg) or enteric-coated aspirin 325?mg + enteric-coated omeprazole 40?mg - a randomised, phase 1, crossover study.?Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013;38(1):62-71. [PMID: 23692061] | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Zokinvy (lonafarnib). Eiger BioPharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA. | ||||
| 46 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Adempas (riociguat). Bayer Pharmaceutical Inc, West Haven, CT. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Inlyta (axitinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 49 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 50 | Collet JP, Hulot JS, Pena A, et al. "Cytochrome P450 2C19 polymorphism in young patients treated with clopidogrel after myocardial infarction: a cohort study." Lancet 373 (2009): 309-17. [PMID: 19108880] | ||||
