Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMPI98T)
| Drug Name |
Doxepin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Zonalon; doxepin; Doxepine; Doxepinum [INN-Latin]; Doxepina [INN-Spanish]; Doxepin [USAN]; trans-doxepin; (e)-doxepin; 1668-19-5; Quitaxon; MF 10; UNII-851NLB57HQ; Sinequan; CCRIS 9176; HSDB 3069; Sinequan (TN); Cidoxepina; Cidoxepinum; 851NLB57HQ; 11-(3-(Dimethylamino)propylidene)-6H-dibenz(b,e)oxepine; 11-(3-Dimethylaminopropylidene)-6,11-dihydrodibenz(b,e)oxipin; 11-(3-Dimethylamino-propyliden)-6,11-dihydro-dibenz(b,e)oxipin; N,N-Dimethyldibenz(b,e)oxepin-delta(11(6H),gamma)-propylamine; Cidoxepin [INN]; Curatin; Adapin; Cidoxepin; Doxepina; Doxepinum; Triadapin; Doxepin Hydrochloride; MOLI001594; Adapine (TN); Aponal (TN); Cis-doxepin; Deptran (TN); Doxepin (INN); Doxepin, Hydrochloride; Sinquan (TN); Xepin (TN); Zonalon (TN); Doxepin (Z)-isomer; Cis-N-(3-(6H-Dibenz(b,e)oxepin-11-yliden)propyl)-N,N-dimethylamin; (3E)-3-(6H-benzo[c][1]benzoxepin-11-ylidene)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine; (3E)-3-dibenzo[b,e]oxepin-11(6H)-ylidene-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine; (3Z)-3-(6H-benzo[c][1]benzoxepin-11-ylidene)-N,N-di(methyl)propan-1-amine; (3Z)-3-(6H-benzo[c][1]benzoxepin-11-ylidene)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine; (3Z)-3-dibenzo[b,e]oxepin-11(6H)-ylidene-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine; (Z)-Doxepin; 3-(6H-benzo[c][1]benzoxepin-11-ylidene)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine; 3-Dibenz[b,e]oxepin-11(6H)-ylidene-N,N-dimethyl-1-propanamine; 3-dibenzo[b,e]oxepin-11(6H)-ylidene-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine; [11C]doxepin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antidepressants
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
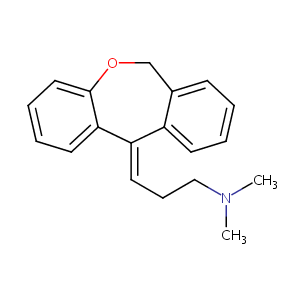 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 279.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 4.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Anxiety | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Doxepin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Doxepin (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Doxepin FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 1225). | ||||
| 3 | New zealand perfalgan report | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Virtanen R, Scheinin M, Iisalo E: Single dose pharmacokinetics of doxepin in healthy volunteers. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 1980 Nov;47(5):371-6. | ||||
| 6 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 7 | Nelis HJ, De Leenheer AP: Metabolism of minocycline in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 1982 Mar-Apr;10(2):142-6. | ||||
| 8 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 9 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 10 | Novel therapeutic usage of low-dose doxepin hydrochloride. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007 Aug;16(8):1295-305. | ||||
| 11 | The N-demethylation of the doxepin isomers is mainly catalyzed by the polymorphic CYP2C19. Pharm Res. 2002 Jul;19(7):1034-7. | ||||
| 12 | Doxepin inhibits CYP2D6 activity in vivo. Pol J Pharmacol. 2004 Jul-Aug;56(4):491-4. | ||||
| 13 | Contributions of CYP2D6, CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 to the biotransformation of E- and Z-doxepin in healthy volunteers. Pharmacogenetics. 2002 Oct;12(7):571-80. | ||||
| 14 | In vitro detection of drug-induced phospholipidosis using gene expression and fluorescent phospholipid based methodologies. Toxicol Sci. 2007 Sep;99(1):162-73. | ||||
| 15 | Effect of common medications on the expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptors in liver tissue. Arch Toxicol. 2020 Dec;94(12):4037-4041. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02869-1. Epub 2020 Aug 17. | ||||
| 16 | Glutathione S-transferase pi as a target for tricyclic antidepressants in human brain. Acta Biochim Pol. 2004;51(1):207-12. | ||||
| 17 | Ciraulo DA, Shader RI "Fluoxetine drug-drug interactions: I. Antidepressants and antipsychotics." J Clin Psychopharmacol 10 (1990): 48-50. [PMID: 1968472] | ||||
| 18 | Achamallah NS "Visual hallucinations after combining fluoxetine and dextromethorphan ." Am J Psychiatry 149 (1992): 1406. [PMID: 1530079] | ||||
| 19 | Spiker DG, Pugh DD "Combining tricyclic and monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressants." Arch Gen Psychiatry 33 (1976): 828-30. [PMID: 942286] | ||||
| 20 | Bhatara VS, Magnus RD, Paul KL, Preskorn SH "Serotonin syndrome induced by venlafaxine and fluoxetine: a case study in polypharmacy and potential pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic mechanisms." Ann Pharmacother 32 (1998): 432-6. [PMID: 9562139] | ||||
| 21 | Cohen MA, Alfonso CA, Mosquera M. Development of urinary retention during treatment with clozapine and meclizine [published correction appears in Am J Psychiatry 1994 Jun;151(6):952]. Am J Psychiatry. 1994;151(4):619-620. [PMID: 8147469] | ||||
| 22 | Kulik AV, Wilbur R "Delirium and stereotypy from anticholinergic antiparkinson drugs." Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 6 (1982): 75-82. [PMID: 7202232] | ||||
| 23 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 25 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 26 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Xospata (gilteritinib). Astellas Pharma US, Inc, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 28 | Vizcaychipi MP, Walker S, Palazzo M "Serotonin syndrome triggered by tramadol." Br J Anaesth 99 (2007): 919. [PMID: 18006535] | ||||
| 29 | Gunston GD, Mehta U "Potentially serious drug interactions with grapefruit juice." S Afr Med J 90 (2000): 41. [PMID: 10721388] | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 31 | Ball P "Quinolone-induced QT interval prolongation: a not-so-unexpected class effect." J Antimicrob Chemother 45 (2000): 557-9. [PMID: 10797074] | ||||
| 32 | Dupont H, Timsit JF, Souweine B, Gachot B, Wolff M, Regnier B "Torsades de pointe probably related to sparfloxacin." Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 15 (1996): 350-1. [PMID: 8781892] | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 34 | Multum Information Services, Inc. Expert Review Panel. | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Daurismo (glasdegib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 36 | Cole JM, Sheehan AH, Jordan JK "Concomitant use of ipratropium and tiotropium in chronic obstructive plmonary disease." Ann Pharmacother 46 (2012): 1717-21. [PMID: 23170031] | ||||
| 37 | Edelbroek PM, Zitman FG, Knoppert-van der Klein EA, van Putten PM, de Wolff FA "Therapeutic drug monitoring of amitriptyline: impact of age, smoking and contraceptives on drug and metabolite levels in bulimic women." Clin Chim Acta 165 (1987): 177-87. [PMID: 3652444] | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Austedo (deutetrabenazine). Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, North Wales, PA. | ||||
| 39 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Myrbetriq (mirabegron). Astellas Pharma US, Inc, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 41 | Boyer EW, Shannon M "The serotonin syndrome." N Engl J Med 352 (2005): 1112-20. [PMID: 15784664] | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Rukobia (fostemsavir). ViiV Healthcare, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Stribild (cobicistat/elvitegravir/emtricitabine/tenofov). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 44 | Anson BD, Weaver JG, Ackerman MJ, et al. "Blockade of HERG channels by HIV protease inhibitors." Lancet 365 (2005): 682-686. [PMID: 15721475] | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Givlaari (givosiran). Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Orladeyo (berotralstat). BioCryst Pharmaceuticals Inc, Durham, NC. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Xalkori (crizotinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Vizimpro (dacomitinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 49 | Product Information. Tagrisso (osimertinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Retevmo (selpercatinib). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 51 | Abernethy DR, Wesche DL, Barbey JT, et al. "Stereoselective halofantrine disposition and effect: concentration-related QTc prolongation." Br J Clin Pharmacol 51 (2001): 231-7. [PMID: 11298069] | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate (hydroxychloroquine). Prasco Laboratories, Cincinnati, OH. | ||||
| 53 | Ohnishi K, Yoshida H, Shigeno K, et al. "Prolongation of the QT interval and ventricular tachycardia in patients treated with arsenic trioxide for acute promyelocytic leukemia." Ann Intern Med 133 (2000): 881-5. [PMID: 11103058] | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Braftovi (encorafenib). Array BioPharma Inc., Boulder, CO. | ||||
| 55 | Product Information. Zulresso (brexanolone). Sage Therapeutics, Inc., Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 56 | Product Information. Addyi (flibanserin). Sprout Pharmaceuticals, Raleigh, NC. | ||||
| 57 | Product Information. Farydak (panobinostat). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 58 | Alvine G, Black DW, Tsuang D "Case of delirium secondary to phenelzine/L-tryptophan combination." J Clin Psychiatry 51 (1990): 311. [PMID: 2365671] | ||||
| 59 | Product Information. Varubi (rolapitant). Tesaro Inc., Waltham, MA. | ||||
| 60 | James WA, Lippmann S "Bupropion: overview and prescribing guidelines in depression." South Med J 84 (1991): 222-4. [PMID: 1899294] | ||||
| 61 | Product Information. Belviq (lorcaserin). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 62 | Morgan JP, Rivera-Calimlim L, Messiha F, Sundaresan PR, Trabert N "Imipramine-mediated interference with levodopa absorption from the gastrointestinal tract in man." Neurology 25 (1975): 1029-34. [PMID: 1237820] | ||||
| 63 | Product Information. Nuplazid (pimavanserin). Accelis Pharma, East Windsor, NJ. | ||||
| 64 | Product Information. Xenleta (lefamulin). Nabriva Therapeutics US, Inc., King of Prussia, PA. | ||||
| 65 | Product Information. Zytiga (abiraterone). Centocor Inc, Malvern, PA. | ||||
| 66 | Bock JL, Nelson JC, Gray S, Jatlow PI "Desipramine hydroxylation: variability and effect of antipsychotic drugs." Clin Pharmacol Ther 33 (1983): 322-8. [PMID: 6130865] | ||||
| 67 | Product Information. Barhemsys (amisulpride). Acacia Pharma, Inc, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 68 | Lee BS "Possibility of hyperpyrexia with antipsychotic and anticholinergic drugs." J Clin Psychiatry 47 (1986): 571. [PMID: 3771507] | ||||
| 69 | Katz MR "Raised serum levels of desipramine with the antiarrhythmic propafenone ." J Clin Psychiatry 52 (1991): 432-3. [PMID: 1938981] | ||||
