Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM72JXH)
| Drug Name |
Losartan
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cozaar; Cozaar (TN); DUP 89; DuP 753; DuP-753; Hyzaar; JMS50MPO89; LOSARTAN POTASSIUM; Lortaan; Losartan (INN); 114798-26-4; C22H23ClN6O; CHEBI:6541; CL23623; Losartan [INN:BAN]; Losartan monopotassium salt; Losartic; Losartic (TN); MK-954; MK954; UNII-JMS50MPO89; [3H]losartan
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antihypertensive Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
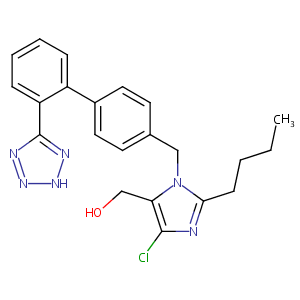 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 422.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 4.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Diabetic kidney disease | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | GB61.Z | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Losartan
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Losartan (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
| DIG |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Formulation |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | Losartan FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 590). | ||||
| 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04343001) Coronavirus Response - Active Support for Hospitalised Covid-19 Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 8 | Radioligand binding assays: application of [(125)I]angiotensin II receptor binding. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;552:131-41. | ||||
| 9 | Controversies of renin-angiotensin system inhibition during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020 Apr 3. | ||||
| 10 | High-affinity interaction of sartans with H+/peptide transporters. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009 Jan;37(1):143-9. | ||||
| 11 | Active transport of the angiotensin-II antagonist losartan and its main metabolite EXP 3174 across MDCK-MDR1 and caco-2 cell monolayers. Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Mar;129(6):1235-43. | ||||
| 12 | Summary of information on human CYP enzymes: human P450 metabolism data. Drug Metab Rev. 2002 Feb-May;34(1-2):83-448. | ||||
| 13 | Substrates, inducers, inhibitors and structure-activity relationships of human Cytochrome P450 2C9 and implications in drug development. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(27):3480-675. | ||||
| 14 | The human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase UGT1A3 is highly selective towards N2 in the tetrazole ring of losartan, candesartan, and zolarsartan. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Sep 15;76(6):763-72. | ||||
| 15 | Drug-drug interaction between losartan and paclitaxel in human liver microsomes with different CYP2C8 genotypes. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015 Jun;116(6):493-8. | ||||
| 16 | Health Canada "Potential risks of cardiovascular and renal adverse events in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with aliskiren (RASILEZ) or aliskiren/hydrochlorothiazide (RASILEZ HCT)." . | ||||
| 17 | Product Information. Diovan (valsartan). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Starlix (nateglinide) Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 19 | Asplund K, Wiholm BE, Lithner F "Glibenclamide-associated hypoglycaemia: a report on 57 cases." Diabetologia 24 (1983): 412-7. [PMID: 6411511] | ||||
| 20 | Goldberg MR, Lo MW, Deutsch PJ, Wilson SE, Mcwilliams EJ, Mccrea JB "Phenobarbital minimally alters plasma concentrations of losartan and its active metabolite e-3174." Clin Pharmacol Ther 59 (1996): 268-74. [PMID: 8653989] | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Synercid (dalfopristin-quinupristin) Rhone-Poulenc Rorer, Collegeville, PA. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Cozaar (losartan). Merck & Co, Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 23 | Aronowitz JS, Chakos MH, Safferman AZ, Lieberman JA "Syncope associated with the combination of clozapine and enalapril." J Clin Psychopharmacol 14 (1994): 429-30. [PMID: 7884028] | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 25 | Warrington SJ, Ankier SI, Turner P "Evaluation of possible interactions between ethanol and trazodone or amitriptyline." Neuropsychobiology 15 (1986): 31-7. [PMID: 3725002] | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Yasmin (drospirenone-ethinyl estradiol) Berlex Laboratories, Richmond, CA. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Korlym (mifepristone). Corcept Therapeutics Incorporated, Menlo Park, CA. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Kalydeco (ivacaftor). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 30 | Ban TA "Drug interactions with psychoactive drugs." Dis Nerv Syst 36 (1975): 164-6. [PMID: 1116424] | ||||
| 31 | Auclair B, Berning SE, Huitt GA, Peloquin CP "Potential interaction between itraconazole and clarithromycin." Pharmacotherapy 19 (1999): 1439-44. [PMID: 10600094] | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Inspra (eplerenone). Searle, Chicago, IL. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Cozaar (losartan). Merck & Co, Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Priftin (rifapentine). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 36 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 37 | Walmsley RN, White GH, Cain M, McCarthy PJ, Booth J "Hyperkalemia in the elderly." Clin Chem 30 (1984): 1409-12. [PMID: 6744599] | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Samsca (tolvaptan). Otsuka American Pharmaceuticals Inc, Rockville, MD. | ||||
| 39 | Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF "Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: Culprit drugs, prevention and management." Drug Saf 42 (2019): 827-47. [PMID: 30888626] | ||||
| 40 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 41 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 44 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Arava (leflunomide). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 47 | Abad S, Moachon L, Blanche P, Bavoux F, Sicard D, Salmon-Ceron D "Possible interaction between glicazide, fluconazole and sulfamethoxazole resulting in severe hypoglycaemia." Br J Clin Pharmacol 52 (2001): 456-7. [PMID: 11678792] | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Clozaril (clozapine). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
