Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMLHESP)
| Drug Name |
Chlorothiazide
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aldoclor; Alurene; Chloriazid; Chlorosal; Chlorothiazid; Chlorothiazidum; Chlorotiazida; Chlorthiazid; Chlorthiazide; Chlorthiazidum; Chlortiazid; Chlorurit; Chlotride; Chlrosal; Clorotiazida; Clorotiazide; Clotride; Diupres; Diuresal; Diuril; Diurilix; Diurite; Diutrid; Flumen; Minzil; Salisan; Salunil; Saluretil; Saluric; Thiazide; Urinex; Warduzide; Yadalan; Clorotiazide [DCIT]; Component of Aldoclor; Diuril Boluses; C 4911; Chlorothiazidum [INN-Latin]; Clorotiazida [INN-Spanish]; Diuril (TN); Diuril Boluses, Veterinary; Neo-Dema; Sk-chlorothiazide; Chlorothiazide [USAN:INN:BAN]; Diuril, Chlotride, Chlorothiazide; Chlorothiazide (JAN/USP/INN); 2H-1,2,4-Benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide, 6-chloro-, 1,1-dioxide; 6-Chloro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide; 6-Chloro-7-sulfamoyl-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide; 6-chloro-4H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antihypertensive Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
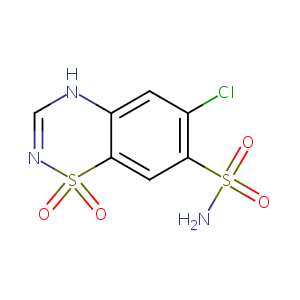 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 295.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -0.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Chronic heart failure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | BD1Z | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Chlorothiazide
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Chlorothiazide (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Chlorothiazide FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4835). | ||||
| 3 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 4 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 5 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 6 | Pharmacogenomic determinants of the cardiovascular effects of dalcetrapib. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2015 Apr;8(2):372-82. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.114.000663. Epub 2015 Jan 11. | ||||
| 7 | A genome-wide association study of caffeine-related sleep disturbance: confirmation of a role for a common variant in the adenosine receptor. Sleep. 2012 Jul 1;35(7):967-75. doi: 10.5665/sleep.1962. | ||||
| 8 | Genome-wide association analyses suggest NELL1 influences adverse metabolic response to HCTZ in African Americans. Pharmacogenomics J. 2014 Feb;14(1):35-40. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2013.3. Epub 2013 Feb 12. | ||||
| 9 | Coffee, CYP1A2 genotype, and risk of myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2006 Mar 8;295(10):1135-41. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.10.1135. | ||||
| 10 | Genome-wide association study of chemotherapeutic agent-induced severe neutropenia/leucopenia for patients in Biobank Japan. Cancer Sci. 2013 Aug;104(8):1074-82. doi: 10.1111/cas.12186. Epub 2013 Jun 10. | ||||
| 11 | Genome-wide association study identifies ephrin type A receptors implicated in paclitaxel induced peripheral sensory neuropathy. J Med Genet. 2013 Sep;50(9):599-605. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-101466. Epub 2013 Jun 17. | ||||
| 12 | Factor V Leiden mutation and thromboembolism risk in women receiving adjuvant tamoxifen for breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010 Jul 7;102(13):942-9. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djq211. Epub 2010 Jun 16. | ||||
| 13 | Localization of diuretic effects along the loop of Henle: an in vivo microperfusion study in rats. Clin Sci (Lond). 2000 Apr;98(4):481-8. | ||||
| 14 | ABCG2 modulates chlorothiazide permeability--in vitro-characterization of its interactions. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2012;27(3):349-53. | ||||
| 15 | Overlapping in vitro and in vivo specificities of the organic anion transporters OAT1 and OAT3 for loop and thiazide diuretics. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008 Apr;294(4):F867-73. | ||||
| 16 | Dean S, Kendall MJ, Potter S, Thompson MH, Jackson DA "Nadolol in combination with indapamide and xipamide in resistant hypertensives." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 28 (1985): 29-33. [PMID: 3987783] | ||||
| 17 | Leary WP, Reyes AJ "Drug interactions with diuretics." S Afr Med J 65 (1984): 455-61. [PMID: 6701709] | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Multaq (dronedarone). sanofi-aventis , Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 19 | FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration "FDA Drug Safety Communication: Low magnesium levels can be associated with long-term use of proton pump inhibitor drugs (PPIs).". | ||||
| 20 | Aronowitz JS, Chakos MH, Safferman AZ, Lieberman JA "Syncope associated with the combination of clozapine and enalapril." J Clin Psychopharmacol 14 (1994): 429-30. [PMID: 7884028] | ||||
| 21 | Muller FO, Schall R, Devaal AC, Groenewoud G, Hundt HKL, Middle MV "Influence of meloxicam on furosemide pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy volunteers." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 48 (1995): 247-51. [PMID: 7589049] | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Savella (milnacipran). Forest Pharmaceuticals, St. Louis, MO. | ||||
| 23 | Ban TA "Drug interactions with psychoactive drugs." Dis Nerv Syst 36 (1975): 164-6. [PMID: 1116424] | ||||
| 24 | Beermann B, Groschinsky-Grind M "Enhancement of the gastrointestinal absorption of hydrochlorothiazide by propantheline." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 13 (1978): 385-7. [PMID: 668798] | ||||
| 25 | Burnakis TG, Mioduch HJ "Combined therapy with captopril and potassium supplementation: a potential for hyperkalemia." Arch Intern Med 144 (1984): 2371-2. [PMID: 6391404] | ||||
| 26 | Ohnishi K, Yoshida H, Shigeno K, et al. "Prolongation of the QT interval and ventricular tachycardia in patients treated with arsenic trioxide for acute promyelocytic leukemia." Ann Intern Med 133 (2000): 881-5. [PMID: 11103058] | ||||
| 27 | Cohen J "Long-term efficacy and safety of terazosin alone and in combination with other antihypertensive agents." Am Heart J 122 (1991): 919-25. [PMID: 1678923] | ||||
| 28 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Clozaril (clozapine). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 30 | Antonelli D, Atar S, Freedberg NA, Rosenfeld T "Torsade de pointes in patients on chronic amiodarone treatment: contributing factors and drug interactions." Isr Med Assoc J 7 (2005): 163-5. [PMID: 15792261] | ||||
