Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMRL3AB)
| Drug Name |
Famotidine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Pepcid; famotidine; 76824-35-6; Pepcid AC; Pepcidine; Quamatel; Gastridin; Famodil; Dispromil; Pepdine; Digervin; Gaster; Fluxid; Pepdul; Pepcid RPD; Famulcer; Supertidine; Pepcidina; Fagastine; Whitidin; Farmotex; Peptifam; Ferotine; Dispronil; Tairal; Sigafam; Famtac; Durater; Yamarin; Pepzan; Famoxal; Evatin; Weimok; Pepdif; Fudone; Fanosin; Fanobel; Duovel; Fibonel; Fadine; Dipsin; Ganor; Fadin; Dinul; Fanox; Fadyn; Famox; Famo; Nu-Famotidine; Pepcidin Rapitab; Sedanium-R; Dibrit 40; Famotidinum [Latin]; PEPCID; Famotidina [Spanish]; Apogastine; Antodine; Bestidine; Amfamox; Blocacid; Brolin; Cepal; Confobos; Cronol; Cuantin; Famocid; Famodar; Famodin; Famodine; Famogard; Famonit; Famopsin; Famos; Famosan; Famotal; Famotep; Famotin; Famovane; Famowal; Gastridan; Gastrion; Gastro; Gastrodomina; Gastrofam; Gastropen; Gastrosidin; Hacip; Huberdina; Ingastri; Invigan; Lecedil; Logos; Mensoma; Midefam; Mosul; Motiax; Muclox; Neocidine; Nevofam; Notidin; Nulceran; Nulcerin; Panalba; Pepcidac; Pepcidin; Pepfamin; Peptan; Peptidin; Purifam; Quamtel; Renapepsa; Restadin; Rogasti; Rubacina; Tamin; Tipodex; Topcid; Ulcatif; Ulceprax; Ulcofam; Ulfagel; Ulfam; Ulfamid; Ulfinol; Ulgarine; Vagostal; FAMOTIDINE PRESERVATIVE FREE; FAMOTIDINE PRESERVATIVE FREE IN PLASTIC CONTAINER; Mylanta AR; PEPCID COMPLETE; PEPCID PRESERVATIVE FREE; PEPCID PRESERVATIVE FREE IN PLASTIC CONTAINER; Pepcid AC Gelcaps; PepcidRPD; F 6889; F0530; L 643341; MK 208; YM 11170; Apo-Famotidine; HS-0054; MK-208; Novo-Famotidine; Pepcid (TN); Pepcidine (TN); YM-11170; YM-1170; Famotidine [USAN:BAN:INN:JAN]; Propanimidamide, 3-[[[2-[aminoiminomethyl)amino]-4-thiazoyl]methyl]thio]-N-(aminosulfonyl); N'-(Aminosulfonyl)-3-([2-(diaminomethyleneamino)-4-thiazolyl]methylthio)propanamidine; (1-Amino-3-(((2-((diaminomethylene)amino)-4-thiazolyl)methyl)thio)propylidene)sulfamide; (1Z)-3-[({2-[(diaminomethylidene)amino]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl}methyl)sulfanyl]-N'-sulfamoylpropanimidamide; (1Z)-N'-(aminosulfonyl)-3-[({2-[(diaminomethylidene)amino]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl}methyl)thio]propanimidamide; 3-(2-Guanidinothiazol-4-ylmethylthio)-N1-sulfamoylpropionamide; 3-[({2-[(diaminomethylidene)amino]-1,3-thiazol-4-yl}methyl)sulfanyl]-N-sulfamoylpropanimidamide; 3-[[2-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methylsulfanyl]-N'-sulfamoylpro; 3-[[2-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methylsulfanyl]-N'-sulfamoylpropanimidamide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiulcer Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
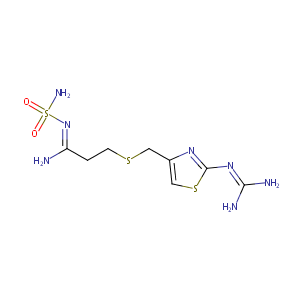 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 337.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -0.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Famotidine (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Famotidine FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7074). | ||||
| 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04370262) Multi-site Adaptive Trials Using Hydroxycholoroquine for COVID-19. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 8 | Histamine H1 and H2 receptor antagonists accelerate skin barrier repair and prevent epidermal hyperplasia induced by barrier disruption in a dry environment. J Invest Dermatol. 2001 Feb;116(2):261-5. | ||||
| 9 | Different transport properties between famotidine and cimetidine by human renal organic ion transporters (SLC22A). Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Oct 25;503(1-3):25-30. | ||||
| 10 | A species difference in the transport activities of H2 receptor antagonists by rat and human renal organic anion and cation transporters. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Oct;315(1):337-45. | ||||
| 11 | Initial 48-hour acid inhibition by intravenous infusion of omeprazole, famotidine, or both in relation to cytochrome P450 2C19 genotype status. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Nov;80(5):539-48. | ||||
| 12 | Famotidine has a neuroprotective effect on MK-801 induced toxicity via the Akt/GSK-3/-catenin signaling pathway in the SH-SY5Y cell line. Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Dec 1;314:108823. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108823. Epub 2019 Sep 26. | ||||
| 13 | Increased immunoreactivity and concentration of basic fibroblast growth factor in lansoprazole-treated gastric mucosa. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1995;21 Suppl 1:S24-9. | ||||
| 14 | Effects of three H2-receptor antagonists (cimetidine, famotidine, ranitidine) on serum gastrin level. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 2002;22(2):29-35. | ||||
| 15 | Systems pharmacological analysis of drugs inducing stevens-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 May 18;28(5):927-34. doi: 10.1021/tx5005248. Epub 2015 Apr 3. | ||||
| 16 | Hyperprolactinaemia during famotidine therapy. Lancet. 1993 Oct 2;342(8875):868. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92729-d. | ||||
| 17 | Albin H, Vincon G, Begaud B, Bistue C, Perez P "Effect of aluminum phosphate on the bioavailability of ranitidine." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 32 (1987): 97-9. [PMID: 3582475] | ||||
| 18 | Honig PK, Gillespie BK "Clinical significance of pharmacokinetic drug interactions with over-the-counter (OTC) drugs." Clin Pharmacokinet 35 (1998): 167-71. [PMID: 9784931] | ||||
| 19 | Dey NG, Castleden CM, Ward J, et al "The effect of cimetidine on tolbutamide kinetics." Br J Clin Pharmacol 16 (1983): 438-40. [PMID: 6626438] | ||||
| 20 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 21 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 22 | Alffenaar JW, van Assen S, van der Werf TS, Kosterink JG, Uges DR "Omeprazole significantly reduces posaconazole serum trough level." Clin Infect Dis 48 (2009): 839. [PMID: 19220151] | ||||
| 23 | Anderson JR, Poklis A, Slavin RG "A fatal case of theophylline intoxication." Arch Intern Med 143 (1983): 559-60. [PMID: 6830388] | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Spectracef (cefditoren). TAP Pharmaceuticals Inc, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 26 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 27 | Blum RA, D'Andrea DT, Florentino BM, et al "Increased gastric pH and the bioavailability of fluconazole and ketoconazole." Ann Intern Med 114 (1991): 755-7. [PMID: 2012358] | ||||
| 28 | Adachi M, Hinatsu Y, et.al "Improved dissolution and absorption of ketoconazole in the presence of organic acids as pH-modifiers." Eur J Pharm Sci 76 (2015): 225-30. [PMID: 25988287] | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Harvoni (ledipasvir-sofosbuvir). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Lexiva (fosamprenavir). GlaxoSmithKline, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Edurant (rilpivirine). Tibotec Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Isentress (raltegravir). Merck & Company Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 33 | Inotsume N, Nishimura M, Nakano M, Fujiyama S, Sato T "The inhibitory effect of probenecid on renal excretion of famotidine in young, healthy volunteers." J Clin Pharmacol 30 (1990): 50-6. [PMID: 2303581] | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Rozerem (ramelteon). Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Lincolnshire, IL. | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Zykadia (ceritinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Calquence (acalabrutinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Gilenya (fingolimod). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Zeposia (ozanimod). Celgene Corporation, Summit, NJ. | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Sprycel (dasatinib). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Effient (prasugrel). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Inlyta (axitinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
