Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMK8U72)
| Drug Name |
Labetalol
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Albetol; Ibidomide; Labetalolum; Labetolol; NORMOZIDE; AH 5158; AH-5158; Labetalol (INN); Labetalol [INN:BAN]; Labetalolum [INN-Latin]; Normodyne (TN); Sch-19927; Trandate (TN); 2-Hydroxy-5-(1-hydroxy-2-((1-methyl-3-phenylpropyl)amino)ethyl)benzamide; 2-hydroxy-5-[1-hydroxy-2-(4-phenylbutan-2-ylamino)ethyl]benzamide; 2-hydroxy-5-{1-hydroxy-2-[(1-methyl-3-phenylpropyl)amino]ethyl}benzamide; 3-Carboxamido-4-hydroxy-alpha-((1-methyl-3-phenylpropylamino)methyl)benzyl alcohol; 5-(1-Hydroxy-2-(1-methyl-3-phenylpropylamino)ethyl)salicylamide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antihypertensive Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
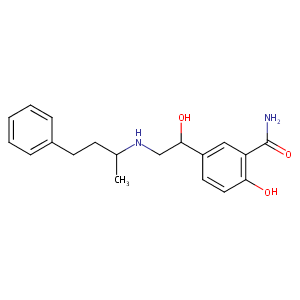 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 328.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Labetalol
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Labetalol (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7207). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Labetalol FDA Label | ||||
| 3 | European Medicines Agency (EMA): DIACOMIT Summary of Product Characteristics | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Clinical pharmacokinetics of labetalol. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1984 Mar-Apr;9(2):157-67. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198409020-00003. | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 8 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 9 | Beta-blockers in the treatment of hypertension: are there clinically relevant differences Postgrad Med. 2009 May;121(3):90-8. | ||||
| 10 | Involvement of influx and efflux transport systems in gastrointestinal absorption of celiprolol. J Pharm Sci. 2009 Jul;98(7):2529-39. | ||||
| 11 | Human intestinal transporter database: QSAR modeling and virtual profiling of drug uptake, efflux and interactions. Pharm Res. 2013 Apr;30(4):996-1007. | ||||
| 12 | Comparison of verapamil, diltiazem, and labetalol on the bioavailability and metabolism of imipramine. J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;32(2):176-83. | ||||
| 13 | Regulation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A1 by progesterone and its impact on labetalol elimination. Xenobiotica. 2008 Jan;38(1):62-75. | ||||
| 14 | Drug Interactions Flockhart Table | ||||
| 15 | Prediction of off-target effects on angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. J Biomol Screen. 2011 Sep;16(8):878-85. doi: 10.1177/1087057111413919. Epub 2011 Aug 22. | ||||
| 16 | Labetalol (AH5158), a competitive alpha- and beta-receptor blocking drug, in the management of hypertension. Aust N Z J Med. 1976 Aug;6(3 Suppl):83-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1976.tb03341.x. | ||||
| 17 | Preclinical pharmacologic properties of dilevalol, an antihypertensive agent possessing selective beta 2 agonist-mediated vasodilation and beta antagonism. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Jun 5;63(19):3I-6I. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90120-3. | ||||
| 18 | Hemodynamic and humoral effects of intravenous dilevalol in patients with moderate hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Jun 5;63(19):34I-37I. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90126-4. | ||||
| 19 | Evaluating the Role of Multidrug Resistance Protein 3 (MDR3) Inhibition in Predicting Drug-Induced Liver Injury Using 125 Pharmaceuticals. Chem Res Toxicol. 2017 May 15;30(5):1219-1229. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00048. Epub 2017 May 4. | ||||
| 20 | Prolactin stimulation by intravenous labetalol is mediated inside the central nervous system. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1982 Jun;16(6):615-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1982.tb03178.x. | ||||
| 21 | Anastassiades CJ "Nifedipine and beta-blocker drugs." Br Med J 281 (1980): 1251-2. [PMID: 6107167] | ||||
| 22 | Dean S, Kendall MJ, Potter S, Thompson MH, Jackson DA "Nadolol in combination with indapamide and xipamide in resistant hypertensives." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 28 (1985): 29-33. [PMID: 3987783] | ||||
| 23 | Amemiya M, Tabei K, Furuya H, Sakairi Y, Asano Y "Pharmacokinetics of carteolol in patients with impaired renal function." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 43 (1992): 417-21. [PMID: 1451723] | ||||
| 24 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 25 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 27 | Haglund K, Seideman P, Colliste P, Borg KO, von Bahr C "Influence of pentobarbital on metoprolol plasma levels." Clin Pharmacol Ther 26 (1979): 326-9. [PMID: 466926] | ||||
| 28 | Hawksworth G, Betts T, Crowe A, et al "Diazepam/beta-adrenoceptor antagonist interactions." Br J Clin Pharmacol 17 Suppl 1 (1984): s69-76. [PMID: 6146341] | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Zylo Filmtab (zileuton). Abbott Pharmaceutical, Abbott Park, IL. | ||||
| 30 | Aronowitz JS, Chakos MH, Safferman AZ, Lieberman JA "Syncope associated with the combination of clozapine and enalapril." J Clin Psychopharmacol 14 (1994): 429-30. [PMID: 7884028] | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 32 | Chapple DJ, Clark JS, Hughes R "Interaction between atracurium and drugs used in anaesthesia." Br J Anaesth 55 Suppl 1 (1983): s17-22. [PMID: 6688011] | ||||
| 33 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 34 | Amchin J, Ereshefsky L, Zarycranski W, Taylor K, Albano D, Klockowski PM "Effect of venlafaxine versus fluoxetine on metabolism of dextromethorphan, a CYP2D6 probe." J Clin Pharmacol 41 (2001): 443-51. [PMID: 11304901] | ||||
| 35 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 36 | Branch RA, Herman RJ "Enzyme induction and beta-adrenergic receptor blocking drugs." Br J Clin Pharmacol 17 (1984): s77-84. [PMID: 6146342] | ||||
| 37 | Chrysant SG "Experience with terazosin administered in combination with other antihypertensive agents." Am J Med 80 (1986): 55-61. [PMID: 2872808] | ||||
| 38 | AbdelRahman SM, Gotschall RR, Kauffman RE, Leeder JS, Kearns GL "Investigation of terbinafine as a CYP2D6 inhibitor in vivo." Clin Pharmacol Ther 65 (1999): 465-72. [PMID: 10340911] | ||||
| 39 | Kirch W, Rose I, Klingmann I, Pabst J, Ohnhaus EE "Interaction of bisoprolol with cimetidine and rifampicin." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 31 (1986): 59-62. [PMID: 2877885] | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 41 | Elsharkawy AM, Schwab U, McCarron B, et al. "Efavirenz induced acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation in a slow drug metaboliser." J Clin Virol 58 (2013): 331-3. [PMID: 23763943] | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 44 | Lancaster DL, Adio RA, Tai KK, Simooya OO, Broadhead GD, Tucker GT, Lennard MS "Inhibition of metoprolol metabolism by chloroquine and other antimalarial drugs." J Pharm Pharmacol 42 (1990): 267-71. [PMID: 1974295] | ||||
| 45 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Clolar (clofarabine). sanofi-aventis, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Gilenya (fingolimod). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 49 | Product Information. Zeposia (ozanimod). Celgene Corporation, Summit, NJ. | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Gleevec (imatinib mesylate). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 51 | Janku I, Perlik F, Tkaczykova M, Brodanova M "Disposition kinetics and concentration-effect relationship of metipranolol in patients with cirrhosis and healthy subjects." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42 (1992): 337-40. [PMID: 1349528] | ||||
| 52 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 53 | Product Information. ReVia (naltrexone). DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Clozaril (clozapine). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 55 | Leor J, Levartowsky D, Sharon C, Farfel Z "Amiodarone and beta-adrenergic blockers: an interaction with metoprolol but not with atenolol." Am Heart J 16 (1988): 206-7. [PMID: 3394625] | ||||
