Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMSQDLE)
| Drug Name |
Flecainide
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
flecainide; 54143-55-4; Flecaine; Tambocor; Flecainida; Flecainidum; (+-)-Flecainide; Flecainidum [INN-Latin]; Flecainida [INN-Spanish]; N-(piperidin-2-ylmethyl)-2,5-bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)benzamide; Flecainide [INN:BAN]; CCRIS 313; Benzamide, N-(2-piperidinylmethyl)-2,5-bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-; C17H20F6N2O3; CHEMBL652; N-(2-Piperidinylmethyl)-2,5-bis(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)benzamide; CHEBI:75984; DJBNUMBKLMJRSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N; NCGC00015443-06; DSSTox_CID_3054; DSSTox_RID_76854; DSSTox_GSID_23054; (-)-Flecainide; Flecaine; Almarytm (TN); Apocard (TN); Ecrinal (TN); Flecainide (INN); Tambocor (TN); N-(piperidin-2-ylmethyl)-2,5-bis[(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)oxy]benzamide; Ic Flecainide
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiarrhythmic Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
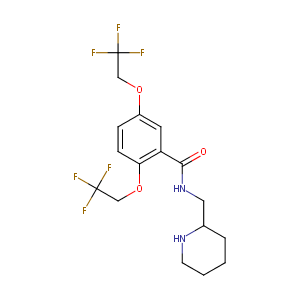 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 414.34 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Flecainide (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2560). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | ||||
| 3 | New antiarrhythmic agents for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2005 May;10(2):311-22. | ||||
| 4 | Metabolism of flecainide. Am J Cardiol. 1984 Feb 27;53(5):41B-51B. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90501-0. | ||||
| 5 | BDDCS predictions, self-correcting aspects of BDDCS assignments, BDDCS assignment corrections, and classification for more than 175 additional drugs | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 8 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 9 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 10 | Flecainide: current status and perspectives in arrhythmia management. World J Cardiol. 2015 Feb 26;7(2):76-85. | ||||
| 11 | A toxicogenomic approach to drug-induced phospholipidosis: analysis of its induction mechanism and establishment of a novel in vitro screening system. Toxicol Sci. 2005 Feb;83(2):282-92. | ||||
| 12 | Determination of phospholipidosis potential based on gene expression analysis in HepG2 cells. Toxicol Sci. 2007 Mar;96(1):101-14. | ||||
| 13 | Palmitate increases the susceptibility of cells to drug-induced toxicity: an in vitro method to identify drugs with potential contraindications in patients with metabolic disease. Toxicol Sci. 2012 Oct;129(2):346-62. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfs208. Epub 2012 Jun 14. | ||||
| 14 | Hertrampf R, Gundert-Remy U, Beckmann J, et al "Elimination of flecainide as a function of urinary flow rate and pH." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 41 (1991): 61-3. [PMID: 1782979] | ||||
| 15 | Product Information. Tibsovo (ivosidenib). Agios Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 16 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 17 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Xospata (gilteritinib). Astellas Pharma US, Inc, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 19 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Arcapta Neohaler (indacaterol). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 21 | Bengtsson B, Fagerstrom PO "Extrapulmonary effects of terbutaline during prolonged administration." Clin Pharmacol Ther 31 (1982): 726-32. [PMID: 7042176] | ||||
| 22 | Ball P "Quinolone-induced QT interval prolongation: a not-so-unexpected class effect." J Antimicrob Chemother 45 (2000): 557-9. [PMID: 10797074] | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Daurismo (glasdegib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Austedo (deutetrabenazine). Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, North Wales, PA. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Ingrezza (valbenazine). Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., San Diego, CA. | ||||
| 26 | EMEA. European Medicines Agency "EPARs. European Union Public Assessment Reports.". | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Myrbetriq (mirabegron). Astellas Pharma US, Inc, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Olysio (simeprevir). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Rukobia (fostemsavir). ViiV Healthcare, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Stribild (cobicistat/elvitegravir/emtricitabine/tenofov). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Fortovase (saquinavir) Roche Laboratories, Nutley, NJ. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 33 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Givlaari (givosiran). Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Orladeyo (berotralstat). BioCryst Pharmaceuticals Inc, Durham, NC. | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Xalkori (crizotinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Vizimpro (dacomitinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Tagrisso (osimertinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 39 | Abernethy DR, Wesche DL, Barbey JT, et al. "Stereoselective halofantrine disposition and effect: concentration-related QTc prolongation." Br J Clin Pharmacol 51 (2001): 231-7. [PMID: 11298069] | ||||
| 40 | Harper KM, Knapp DJ, Criswell HE, Breese GR "Vasopressin and alcohol: A multifaceted relationship." Psychopharmacology (Berl) 235 (2018): 3363-79. [PMID: 32936259] | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Farydak (panobinostat). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Zeposia (ozanimod). Celgene Corporation, Summit, NJ. | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Sprycel (dasatinib). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Varubi (rolapitant). Tesaro Inc., Waltham, MA. | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Belviq (lorcaserin). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Nuplazid (pimavanserin). Accelis Pharma, East Windsor, NJ. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Macrilen (macimorelin). Aeterna Zentaris, Charleston, SC. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Xenleta (lefamulin). Nabriva Therapeutics US, Inc., King of Prussia, PA. | ||||
| 49 | Product Information. Zytiga (abiraterone). Centocor Inc, Malvern, PA. | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Barhemsys (amisulpride). Acacia Pharma, Inc, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 51 | Iannini PB "Cardiotoxicity of macrolides, ketolides and fluoroquinolones that prolong the QTc interval." Expert Opin Drug Saf 1 (2002): 121-8. [PMID: 12904146] | ||||
