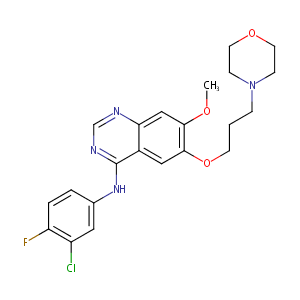
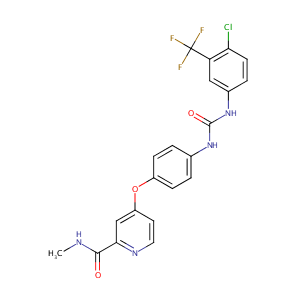
| 1 |
Recurrent recessive mutation in deoxyguanosine kinase causes idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension.Hepatology. 2016 Jun;63(6):1977-86. doi: 10.1002/hep.28499. Epub 2016 Mar 31.
|
| 2 |
Gefitinib FDA Label
|
| 3 |
URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4941).
|
| 4 |
Sorafenib FDA Label
|
| 5 |
URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5711).
|
| 6 |
Synergistic antitumor effect of S-1 and the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines: role of gefitinib-induced down-regulation of thymidylate synthase. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Mar;7(3):599-606.
|
| 7 |
Frankincense myrrh attenuates hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating tumor blood vessel development through multiple epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated signaling pathways. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Feb 15;14(2):450-477. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i2.450.
|
| 8 |
EGFR inhibitors enhanced the susceptibility to NK cell-mediated lysis of lung cancer cells. J Immunother. 2011 May;34(4):372-81. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e31821b724a.
|
| 9 |
Overcoming acquired resistance of gefitinib in lung cancer cells without T790M by AZD9291 or Twist1 knockdown in vitro and in vivo. Arch Toxicol. 2019 Jun;93(6):1555-1571. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02453-2. Epub 2019 Apr 16.
|
| 10 |
DNA repair gene polymorphisms and benefit from gefitinib in never-smokers with lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 2011 Jul 15;117(14):3201-8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25863. Epub 2011 Jan 24.
|
| 11 |
Gefitinib ('Iressa', ZD1839) and new epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Br J Cancer. 2004 Feb 9;90(3):566-72.
|
| 12 |
Gefitinib-phenytoin interaction is not correlated with the C-erythromycin breath test in healthy male volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Aug;68(2):226-37.
|
| 13 |
Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family in multidrug resistance: A review of the past decade. Cancer Lett. 2016 Jan 1;370(1):153-64.
|
| 14 |
Contribution of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 to the disposition of sorafenib and sorafenib-glucuronide. Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Mar 15;19(6):1458-66.
|
| 15 |
Differential metabolism of gefitinib and erlotinib by human cytochrome P450 enzymes. Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Jun 15;13(12):3731-7.
|
| 16 |
Pharmacokinetic drug interactions of gefitinib with rifampicin, itraconazole and metoprolol. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005;44(10):1067-81.
|
| 17 |
Pharmacogenetics of ABCG2 and adverse reactions to gefitinib. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006 Dec 6;98(23):1739-42.
|
| 18 |
Dasatinib (BMS-354825) selectively induces apoptosis in lung cancer cells dependent on epidermal growth factor receptor signaling for survival. Cancer Res. 2006 Jun 1;66(11):5542-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4620.
|
| 19 |
Identification of genes linked to gefitinib treatment in prostate cancer cell lines with or without resistance to androgen: a clue to application of gefitinib to hormone-resistant prostate cancer. Oncol Rep. 2006 Jun;15(6):1453-60.
|
| 20 |
Interference with bile salt export pump function is a susceptibility factor for human liver injury in drug development. Toxicol Sci. 2010 Dec; 118(2):485-500.
|
| 21 |
Effects and mechanisms of betulinic acid on improving EGFR TKI-resistance of lung cancer cells. Environ Toxicol. 2018 Nov;33(11):1153-1159.
|
| 22 |
Antiproliferative effects of gefitinib are associated with suppression of E2F-1 expression and telomerase activity. Anticancer Res. 2006 Sep-Oct;26(5A):3387-91.
|
| 23 |
Leptomycin B reduces primary and acquired resistance of gefitinib in lung cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 Nov 15;335:16-27. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.09.017. Epub 2017 Sep 21.
|
| 24 |
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors activate autophagy as a cytoprotective response in human lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e18691. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018691. Epub 2011 Jun 2.
|
| 25 |
ZD1839 induces p15INK4b and causes G1 arrest by inhibiting the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 May;6(5):1579-87. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0814.
|
| 26 |
Reactive metabolite of gefitinib activates inflammasomes: implications for gefitinib-induced idiosyncratic reaction. J Toxicol Sci. 2020;45(11):673-680. doi: 10.2131/jts.45.673.
|
| 27 |
Systems pharmacological analysis of drugs inducing stevens-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 May 18;28(5):927-34. doi: 10.1021/tx5005248. Epub 2015 Apr 3.
|
| 28 |
Bidirectional cross talk between ERalpha and EGFR signalling pathways regulates tamoxifen-resistant growth. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006 Mar;96(2):131-46. doi: 10.1007/s10549-005-9070-2. Epub 2005 Oct 27.
|
| 29 |
Epidermal growth factor receptor activity determines response of colorectal cancer cells to gefitinib alone and in combination with chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Oct 15;11(20):7480-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0328.
|
| 30 |
Implication of the insulin-like growth factor-IR pathway in the resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells to treatment with gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2007 May 1;13(9):2795-803. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2077.
|
| 31 |
Evidence of securin-mediated resistance to gefitinib-induced apoptosis in human cancer cells. Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Apr 25;203(2):412-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2013.03.011. Epub 2013 Mar 22.
|
| 32 |
Crosstalk between alveolar macrophages and alveolar epithelial cells/fibroblasts contributes to the pulmonary toxicity of gefitinib. Toxicol Lett. 2021 Mar 1;338:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2020.11.011. Epub 2020 Nov 25.
|
| 33 |
Cytotoxicity of 34 FDA approved small-molecule kinase inhibitors in primary rat and human hepatocytes. Toxicol Lett. 2018 Jul;291:138-148. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.04.010. Epub 2018 Apr 12.
|
| 34 |
Growth of hormone-dependent MCF-7 breast cancer cells is promoted by constitutive caveolin-1 whose expression is lost in an EGF-R-mediated manner during development of tamoxifen resistance. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Feb;119(3):575-91. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0355-8. Epub 2009 Mar 15.
|
| 35 |
Dihydromyricetin suppresses tumor growth via downregulation of the EGFR/Akt/survivin signaling pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023 Jun;37(6):e23328. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23328. Epub 2023 Feb 19.
|
| 36 |
The anti-cancer drug gefitinib accelerates Fas-mediated apoptosis by enhancing caspase-8 activation in cancer cells. J Toxicol Sci. 2019;44(6):435-440. doi: 10.2131/jts.44.435.
|
| 37 |
Autophagy Inhibition Overcomes the Antagonistic Effect Between Gefitinib and Cisplatin in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Non--Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Clin Lung Cancer. 2015 Sep;16(5):e55-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Apr 2.
|
| 38 |
Nrf2 but not autophagy inhibition is associated with the survival of wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor non-small cell lung cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 1;310:140-149. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Sep 14.
|
| 39 |
Association of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 inhibition in in vitro assays with drug-induced liver injury. J Toxicol Sci. 2021;46(4):167-176. doi: 10.2131/jts.46.167.
|
| 40 |
Susceptibility to natural killer cell-mediated lysis of colon cancer cells is enhanced by treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors through UL16-binding protein-1 induction. Cancer Sci. 2012 Jan;103(1):7-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.02109.x. Epub 2011 Nov 15.
|
| 41 |
Combined tamoxifen and gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer shows antiproliferative effects. Biomed Pharmacother. 2010 Feb;64(2):88-92. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2009.06.010. Epub 2009 Oct 23.
|
| 42 |
Inorganic arsenic exposure promotes malignant progression by HDAC6-mediated down-regulation of HTRA1. J Appl Toxicol. 2023 Aug;43(8):1214-1224. doi: 10.1002/jat.4457. Epub 2023 Mar 11.
|
| 43 |
A high-throughput screen for teratogens using human pluripotent stem cells. Toxicol Sci. 2014 Jan;137(1):76-90. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft239. Epub 2013 Oct 23.
|
| 44 |
Inhibition of SREBP increases gefitinib sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 9;7(32):52392-52403.
|
| 45 |
The K-Ras effector p38 MAPK confers intrinsic resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors by stimulating EGFR transcription and EGFR dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 8;292(36):15070-15079. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.779488. Epub 2017 Jul 24.
|
| 46 |
Slug confers resistance to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Apr 15;183(8):1071-9. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201009-1440OC. Epub 2010 Oct 29.
|
| 47 |
Identification of protein expression alterations in gefitinib-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma: PCNT and mPR play key roles in the development of gefitinib-associated resistance. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Nov 1;288(3):359-73. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.08.008. Epub 2015 Aug 20.
|
| 48 |
Induction of CYP1A1 increases gefitinib-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in A549 cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2017 Oct;44:36-43.
|
| 49 |
Prediction of sensitivity of advanced non-small cell lung cancers to gefitinib (Iressa, ZD1839). Hum Mol Genet. 2004 Dec 15;13(24):3029-43. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh331. Epub 2004 Oct 20.
|
| 50 |
The transcription factor FOXO3a is a crucial cellular target of gefitinib (Iressa) in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Dec;6(12 Pt 1):3169-79. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0507.
|
| 51 |
Aurora-A promotes gefitinib resistance via a NF-B signaling pathway in p53 knockdown lung cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Feb 11;405(2):168-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.01.001. Epub 2011 Jan 7.
|
| 52 |
BIM induction of apoptosis triggered by EGFR-sensitive and resistance cell lines of non-small-cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 2011 Jun;28(2):572-7. doi: 10.1007/s12032-010-9470-y. Epub 2010 Mar 17.
|
| 53 |
E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF180 reduces sensitivity of triple-negative breast cancer cells to Gefitinib by downregulating RAD51. Chem Biol Interact. 2022 Feb 25;354:109798. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.109798. Epub 2022 Jan 6.
|
| 54 |
Increases of amphiregulin and transforming growth factor-alpha in serum as predictors of poor response to gefitinib among patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Res. 2005 Oct 15;65(20):9176-84. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1556.
|
| 55 |
Novel carbocyclic curcumin analog CUR3d modulates genes involved in multiple apoptosis pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Dec 5;242:107-22.
|
| 56 |
Destruxin B inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth through modulation of the Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Toxicol In Vitro. 2014 Jun;28(4):552-61. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Jan 13.
|
| 57 |
The kinase inhibitor sorafenib induces cell death through a process involving induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;27(15):5499-513. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01080-06. Epub 2007 Jun 4.
|
| 58 |
Sorafenib induces apoptosis of AML cells via Bim-mediated activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Leukemia. 2008 Apr;22(4):808-18. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2405098. Epub 2008 Jan 17.
|
| 59 |
Ovatodiolide suppresses yes-associated protein 1-modulated cancer stem cell phenotypes in highly malignant hepatocellular carcinoma and sensitizes cancer cells to chemotherapy in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. 2018 Sep;51:74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2018.04.010. Epub 2018 Apr 24.
|
| 60 |
Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase signaling.Mol Cancer Ther.2008 Oct;7(10):3129-40.
|
| 61 |
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Current treatment options and future directions. J Nasopharyng Carcinoma, 2014, 1(16): e16.
|
| 62 |
Multidrug resistance protein 2 implicates anticancer drug-resistance to sorafenib. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(3):433-5.
|
| 63 |
Breast cancer resistance protein and P-glycoprotein limit sorafenib brain accumulation. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Feb;9(2):319-26.
|
| 64 |
Double-transduced MDCKII cells to study human P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) interplay in drug transport across the blood-brain barrier. Mol Pharm. 2011 Apr 4;8(2):571-82.
|
| 65 |
Upregulation of histone acetylation reverses organic anion transporter 2 repression and enhances 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma
|
| 66 |
Rlip76 transports sunitinib and sorafenib and mediates drug resistance in kidney cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010 Mar 15;126(6):1327-38.
|
| 67 |
Interaction of sorafenib and cytochrome P450 isoenzymes in patients with advanced melanoma: a phase I/II pharmacokinetic interaction study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011 Nov;68(5):1111-8.
|
| 68 |
Ontogeny and sorafenib metabolism. Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Oct 15;18(20):5788-95.
|
| 69 |
Drug Interactions Flockhart Table
|
| 70 |
Pharmacokinetic interaction involving sorafenib and the calcium-channel blocker felodipine in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma. Invest New Drugs. 2011 Dec;29(6):1511-4.
|
| 71 |
Differential inhibition of human CYP2C8 and molecular docking interactions elicited by sorafenib and its major N-oxide metabolite. Chem Biol Interact. 2021 Apr 1;338:109401. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109401. Epub 2021 Feb 5.
|
| 72 |
The Enhanced metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells with sorafenib resistance. PLoS One. 2013 Nov 11;8(11):e78675. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078675. eCollection 2013.
|
| 73 |
Sorafenib induces growth suppression in mouse models of gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Jan;8(1):152-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0553.
|
| 74 |
Down-regulation of CYLD as a trigger for NF-B activation and a mechanism of apoptotic resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2011 Jan;38(1):121-31.
|
| 75 |
Sorafenib induces apoptotic cell death in human non-small cell lung cancer cells by down-regulating mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-dependent survivin expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Aug 1;82(3):216-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.04.011. Epub 2011 May 13.
|
| 76 |
Differential effects of arsenic trioxide on chemosensitization in human hepatic tumor and stellate cell lines. BMC Cancer. 2012 Sep 10;12:402.
|
| 77 |
The multikinase inhibitor sorafenib potentiates TRAIL lethality in human leukemia cells in association with Mcl-1 and cFLIPL down-regulation. Cancer Res. 2007 Oct 1;67(19):9490-500. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0598.
|
| 78 |
Apoptosis induced by the kinase inhibitor BAY 43-9006 in human leukemia cells involves down-regulation of Mcl-1 through inhibition of translation. J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 21;280(42):35217-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506551200. Epub 2005 Aug 18.
|
| 79 |
Sorafenib targets the mitochondrial electron transport chain complexes and ATP synthase to activate the PINK1-Parkin pathway and modulate cellular drug response. J Biol Chem. 2017 Sep 8;292(36):15105-15120. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.783175. Epub 2017 Jul 3.
|
| 80 |
Induction of DNA damage-inducible gene GADD45beta contributes to sorafenib-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2010 Nov 15;70(22):9309-18. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1033. Epub 2010 Nov 9.
|
| 81 |
Growth arrest DNA damage-inducible gene 45 gamma expression as a prognostic and predictive biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 29;6(29):27953-65. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4446.
|
| 82 |
Sorafenib induces apoptosis specifically in cells expressing BCR/ABL by inhibiting its kinase activity to activate the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. Cancer Res. 2009 May 1;69(9):3927-36. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2978. Epub 2009 Apr 14.
|
| 83 |
Synergistic antimetastatic effect of cotreatment with licochalcone A and sorafenib on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the inactivation of MKK4/JNK and uPA expression. Environ Toxicol. 2018 Dec;33(12):1237-1244. doi: 10.1002/tox.22630. Epub 2018 Sep 6.
|
| 84 |
Sorafenib inhibits transforming growth factor 1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis in mouse hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2011 May;53(5):1708-18. doi: 10.1002/hep.24254.
|
| 85 |
Activation of inflammasomes by tyrosine kinase inhibitors of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor: Implications for VEGFR TKIs-induced immune related adverse events. Toxicol In Vitro. 2021 Mar;71:105063. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2020.105063. Epub 2020 Dec 1.
|
| 86 |
Sorafenib is an antagonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Toxicology. 2022 Mar 30;470:153118. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2022.153118. Epub 2022 Feb 3.
|
| 87 |
Sorafenib induces cell death in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by translational downregulation of Mcl-1. Leukemia. 2011 May;25(5):838-47. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.2. Epub 2011 Feb 4.
|
| 88 |
Cell cycle dependent and schedule-dependent antitumor effects of sorafenib combined with radiation. Cancer Res. 2007 Oct 1;67(19):9443-54. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1473.
|
| 89 |
Sorafenib functions to potently suppress RET tyrosine kinase activity by direct enzymatic inhibition and promoting RET lysosomal degradation independent of proteasomal targeting. J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 5;282(40):29230-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703461200. Epub 2007 Jul 30.
|
| 90 |
Synergistic activity of letrozole and sorafenib on breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Nov;124(1):79-88. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0714-5. Epub 2010 Jan 7.
|
| 91 |
Coadministration of sorafenib with rottlerin potently inhibits cell proliferation and migration in human malignant glioma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Dec;319(3):1070-80. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.108621. Epub 2006 Sep 7.
|
| 92 |
Sorafenib induces apoptosis in HL60 cells by inhibiting Src kinase-mediated STAT3 phosphorylation. Anticancer Drugs. 2011 Jan;22(1):79-88. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e32833f44fd.
|
| 93 |
Rap1/B-Raf signaling is activated in neuroendocrine tumors of the digestive tract and Raf kinase inhibition constitutes a putative therapeutic target. Neuroendocrinology. 2007;85(1):45-53. doi: 10.1159/000100508. Epub 2007 Mar 5.
|
| 94 |
Potent activity of ponatinib (AP24534) in models of FLT3-driven acute myeloid leukemia and other hematologic malignancies. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Jun;10(6):1028-35. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-1044. Epub 2011 Apr 11.
|
| 95 |
Inhibition of autophagy potentiates the antitumor effect of the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2012 Aug 1;131(3):548-57. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26374. Epub 2011 Sep 12.
|
| 96 |
Sorafenib inhibits signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling associated with growth arrest and apoptosis of medulloblastomas. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Nov;7(11):3519-26. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0138.
|
| 97 |
Therapeutic targeting of hepatocellular carcinoma cells with antrocinol, a novel, dual-specificity, small-molecule inhibitor of the KRAS and ERK oncogenic signaling pathways. Chem Biol Interact. 2023 Jan 25;370:110329. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110329. Epub 2022 Dec 22.
|
| 98 |
Sorafenib derivatives induce apoptosis through inhibition of STAT3 independent of Raf. Eur J Med Chem. 2011 Jul;46(7):2845-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.04.007. Epub 2011 Apr 14.
|
| 99 |
The multikinase inhibitor sorafenib induces apoptosis in highly imatinib mesylate-resistant bcr/abl+ human leukemia cells in association with signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 inhibition and myeloid cell leukemia-1 down-regulation. Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Sep;72(3):788-95. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.033308. Epub 2007 Jun 26.
|
| 100 |
Arsenic trioxide potentiates the anti-cancer activities of sorafenib against hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting Akt activation. Tumour Biol. 2015 Apr;36(4):2323-34. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2839-3. Epub 2014 Nov 22.
|
| 101 |
Proliferation and survival molecules implicated in the inhibition of BRAF pathway in thyroid cancer cells harbouring different genetic mutations. BMC Cancer. 2009 Oct 31;9:387. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-387.
|
| 102 |
The multikinase inhibitor Sorafenib induces apoptosis and sensitises endometrial cancer cells to TRAIL by different mechanisms. Eur J Cancer. 2010 Mar;46(4):836-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2009.12.025. Epub 2010 Jan 12.
|
| 103 |
Downregulation of stanniocalcin 1 is responsible for sorafenib-induced cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Sci. 2015 Feb;143(2):374-84. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu235. Epub 2014 Nov 3.
|
| 104 |
Sorafenib induces preferential apoptotic killing of a drug- and radio-resistant Hep G2 cells through a mitochondria-dependent oxidative stress mechanism. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Oct;8(20):1904-13. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.20.9436. Epub 2009 Oct 6.
|
| 105 |
Protective effect of sestrin2 against iron overload and ferroptosis-induced liver injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 15;379:114665. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.114665. Epub 2019 Jul 16.
|
| 106 |
Mechanisms of apoptosis induction by simultaneous inhibition of PI3K and FLT3-ITD in AML cells in the hypoxic bone marrow microenvironment. Cancer Lett. 2013 Feb 1;329(1):45-58. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.09.020. Epub 2012 Oct 2.
|
| 107 |
The role of Mcl-1 downregulation in the proapoptotic activity of the multikinase inhibitor BAY 43-9006. Oncogene. 2005 Oct 20;24(46):6861-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208841.
|
| 108 |
Why are most phospholipidosis inducers also hERG blockers?. Arch Toxicol. 2017 Dec;91(12):3885-3895. doi: 10.1007/s00204-017-1995-9. Epub 2017 May 27.
|
| 109 |
The multikinase inhibitor sorafenib induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Asian J Androl. 2010 Jul;12(4):527-34. doi: 10.1038/aja.2010.21. Epub 2010 May 17.
|
| 110 |
Synergistic inhibition of human melanoma proliferation by combination treatment with B-Raf inhibitor BAY43-9006 and mTOR inhibitor Rapamycin. J Transl Med. 2005 Oct 28;3:39. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-3-39.
|
| 111 |
GSK-3beta inhibition enhances sorafenib-induced apoptosis in melanoma cell lines. J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 11;283(2):726-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705343200. Epub 2007 Nov 8.
|
| 112 |
Cytotoxic synergy between the multikinase inhibitor sorafenib and the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in vitro: induction of apoptosis through Akt and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathways. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Sep;5(9):2378-87. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0235.
|
| 113 |
Vorinostat and sorafenib increase ER stress, autophagy and apoptosis via ceramide-dependent CD95 and PERK activation. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008 Oct;7(10):1648-62. doi: 10.4161/cbt.7.10.6623. Epub 2008 Oct 12.
|
| 114 |
TRIM62 silencing represses the proliferation and invasion and increases the chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by affecting the NF-B pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 15;445:116035. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.116035. Epub 2022 Apr 23.
|
| 115 |
Diospyros kaki leaves inhibit HGF/Met signaling-mediated EMT and stemness features in hepatocellular carcinoma. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020 Aug;142:111475. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111475. Epub 2020 Jun 6.
|
| 116 |
Comparative proteomic analysis of SLC13A5 knockdown reveals elevated ketogenesis and enhanced cellular toxic response to chemotherapeutic agents in HepG2 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 1;402:115117. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115117. Epub 2020 Jul 4.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|