Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMM0XGL)
| Drug Name |
Idarubicin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
DMDR; Idamycin; Idarubicina; Idarubicine; Idarubicinum; Zavedos; Idarubicin Hcl; Idarubicin Hcl Pfs; Idarubicin hydrochloride; DM5; I 1656; IMI 30; IMI-30; Idamycin (TN); Idarubicin (INN); Idarubicin [INN:BAN]; Idarubicina [INN-Spanish]; Idarubicine [INN-French]; Idarubicinum [INN-Latin]; Zavedos (TN); (1S,3S)-3-acetyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-alpha-L-lyxo-hexopyranoside; (1s,3s)-3-acetyl-3,5,12-trihydroxy-6,11-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,11-hexahydrotetracen-1-yl 3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-A-l-lyxo-hexopyranoside; (7S,9S)-9-acetyl-7-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-6,9,11-trihydroxy-8,10-dihydro-7H-tetracene-5,12-dione; (7S-cis)-9-Acetyl-7-[(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-alpha-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6,9,11-trihydroxy-5,12-naphthacenedione; 4-DMD; 4-Demethoxydaunomycin; 4-Demethoxydaunorubicin; 4-Desmethoxydaunorubicin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticancer Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammalsBacteria
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
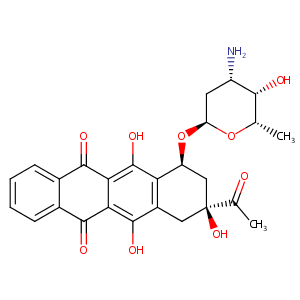 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 497.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Idarubicin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Idarubicin (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | Idarubicin FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7083). | ||||
| 3 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 4 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 5 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 6 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 7 | Human intestinal transporter database: QSAR modeling and virtual profiling of drug uptake, efflux and interactions. Pharm Res. 2013 Apr;30(4):996-1007. | ||||
| 8 | Amonafide L-malate is not a substrate for multidrug resistance proteins in secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2008 Nov;22(11):2110-5. | ||||
| 9 | In vitro evaluation of cytochrome P450-mediated drug interactions between cytarabine, idarubicin, itraconazole and caspofungin. Hematology. 2004 Jun;9(3):217-21. | ||||
| 10 | Quantitative high-throughput profiling of environmental chemicals and drugs that modulate farnesoid X receptor. Sci Rep. 2014 Sep 26;4:6437. doi: 10.1038/srep06437. | ||||
| 11 | The induction of apoptosis by daunorubicin and idarubicin in human trisomic and diabetic fibroblasts. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2008;13(2):182-94. doi: 10.2478/s11658-007-0045-7. Epub 2008 Apr 10. | ||||
| 12 | A Quantitative Approach to Screen for Nephrotoxic Compounds In Vitro. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Apr;27(4):1015-28. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015010060. Epub 2015 Aug 10. | ||||
| 13 | The use of biochemical markers in cardiotoxicity monitoring in patients treated for leukemia. Neoplasma. 2005;52(5):430-4. | ||||
| 14 | Refining the human iPSC-cardiomyocyte arrhythmic risk assessment model. Toxicol Sci. 2013 Dec;136(2):581-94. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft205. Epub 2013 Sep 19. | ||||
| 15 | Product Information. Tibsovo (ivosidenib). Agios Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 16 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 17 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 18 | Product Information. Xospata (gilteritinib). Astellas Pharma US, Inc, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 19 | Multum Information Services, Inc. Expert Review Panel. | ||||
| 20 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Arcapta Neohaler (indacaterol). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 22 | Bengtsson B, Fagerstrom PO "Extrapulmonary effects of terbutaline during prolonged administration." Clin Pharmacol Ther 31 (1982): 726-32. [PMID: 7042176] | ||||
| 23 | Ball P "Quinolone-induced QT interval prolongation: a not-so-unexpected class effect." J Antimicrob Chemother 45 (2000): 557-9. [PMID: 10797074] | ||||
| 24 | Johnson EJ, MacGowan AP, Potter MN, et al "Reduced absorption of oral ciprofloxacin after chemotherapy for haematological malignancy." J Antimicrob Chemother 25 (1990): 837-42. [PMID: 2373666] | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Balversa (erdafitinib). Janssen Products, LP, Horsham, PA. | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Daurismo (glasdegib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Austedo (deutetrabenazine). Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, North Wales, PA. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Ingrezza (valbenazine). Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., San Diego, CA. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Rukobia (fostemsavir). ViiV Healthcare, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 30 | Anson BD, Weaver JG, Ackerman MJ, et al. "Blockade of HERG channels by HIV protease inhibitors." Lancet 365 (2005): 682-686. [PMID: 15721475] | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Arava (leflunomide). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Prolia (denosumab). Amgen USA, Thousand Oaks, CA. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Xalkori (crizotinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Tagrisso (osimertinib). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 35 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 36 | Abernethy DR, Wesche DL, Barbey JT, et al. "Stereoselective halofantrine disposition and effect: concentration-related QTc prolongation." Br J Clin Pharmacol 51 (2001): 231-7. [PMID: 11298069] | ||||
| 37 | Harper KM, Knapp DJ, Criswell HE, Breese GR "Vasopressin and alcohol: A multifaceted relationship." Psychopharmacology (Berl) 235 (2018): 3363-79. [PMID: 32936259] | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Braftovi (encorafenib). Array BioPharma Inc., Boulder, CO. | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Farydak (panobinostat). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Vumerity (diroximel fumarate). Alkermes, Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Gilenya (fingolimod). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Ocrevus (ocrelizumab). Genentech, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Sprycel (dasatinib). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Synribo (omacetaxine). Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, North Wales, PA. | ||||
| 46 | Product Information. Varubi (rolapitant). Tesaro Inc., Waltham, MA. | ||||
| 47 | Product Information. Nuplazid (pimavanserin). Accelis Pharma, East Windsor, NJ. | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Macrilen (macimorelin). Aeterna Zentaris, Charleston, SC. | ||||
| 49 | Product Information. Xenleta (lefamulin). Nabriva Therapeutics US, Inc., King of Prussia, PA. | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Arcalyst (rilonacept). Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc, Tarrytown, NY. | ||||
| 51 | Product Information. Cimzia (certolizumab). UCB Pharma Inc, Smyrna, GA. | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Barhemsys (amisulpride). Acacia Pharma, Inc, Indianapolis, IN. | ||||
| 53 | CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/ "Recommendations of the advisory committtee on immunization practices (ACIP): use of vaccines and immune globulins in persons with altered immunocompetence." MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 42(RR-04) (1993): 1-18. [PMID: 20300058] | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 55 | Iannini PB "Cardiotoxicity of macrolides, ketolides and fluoroquinolones that prolong the QTc interval." Expert Opin Drug Saf 1 (2002): 121-8. [PMID: 12904146] | ||||
