Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM30SGU)
| Drug Name |
Simvastatin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cholestat; Coledis; Colemin; Corolin; Denan; Labistatin; Lipex; Lipovas; Lodales; Medipo; Nivelipol; Pantok; Rendapid; Simovil; Simvastatina; Simvastatine; Simvastatinum; Sinvacor; Sivastin; Synvinolin; Vasotenal; Zocor; Zocord; Simvast CR; Simvastatina [Spanish]; Simvastatine [French]; Simvastatinum [Latin]; MK 0733; MK 733; MK733; TNP00259; DRG-0320; KS-1113; L 644128-000U; MK-0733; MK-733; Simcard (TN); Simlup (TN); Simvacor (TN); Simvastatin & Primycin; Simvastatin, Compactin; Zocor (TN); Simvastatin [USAN:INN:BAN]; Simvastatin (JAN/USP/INN); Zocor, Simlup, Simcard, Simvacor, Simvoget, Zorced, Simvastatin; [(1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxooxan-2-yl]ethyl]-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl] 2,2-dimethylbutanoate; Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-, (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester; Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-, (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-(2-((2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-1-naphthalenyl ester; Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-, (1S,3R,7S,8S,*aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-(2-((2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-1-naphthalenyl ester; (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-{2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxotetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl}-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate; Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-,1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-(tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)-ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester, [1S-[1 alpha,3 alpha,7 beta,8 beta(2S*,4S*),-8a beta; 2,2-Dimethylbutanoic acid (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester; 2,2-Dimethylbutyric acid, 8-ester with (4R,6R)-6-(2-((1S,2S,6R,8S,8aR)-1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-8-hydroxy-2,6-dimethyl-1-naphthyl)ethyl)tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-2H-pyran-2-one
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Anticholesteremic Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
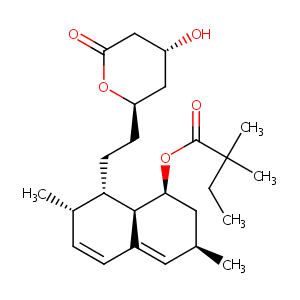 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 418.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 4.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Arteriosclerosis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | BD40 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental Cancer Drug Sensitivity Information
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Simvastatin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Simvastatin (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
| DIG |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Formulation |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
| 1 | Simvastatin FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2955). | ||||
| 3 | Simvastatin pharmacokinetics in healthy Chinese subjects and its relations with CYP2C9, CYP3A5, ABCB1, ABCG2 and SLCO1B1 polymorphisms. Pharmazie. 2013 Feb;68(2):124-8. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Nakajima M, Nakamura S, Tokudome S, Shimada N, Yamazaki H, Yokoi T: Azelastine N-demethylation by cytochrome P-450 (CYP)3A4, CYP2D6, and CYP1A2 in human liver microsomes: evaluation of approach to predict the contribution of multiple CYPs. Drug Metab Dispos. 1999 Dec;27(12):1381-91. | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 8 | Association of the Trp719Arg polymorphism in kinesin-like protein 6 with myocardial infarction and coronary heart disease in 2 prospective trials: the CARE and WOSCOPS trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Jan 29;51(4):435-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.05.057. | ||||
| 9 | Equally potent inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis in human hepatocytes have distinguishable effects on different cytochrome P450 enzymes. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2000 Dec;21(9):353-64. | ||||
| 10 | Human intestinal transporter database: QSAR modeling and virtual profiling of drug uptake, efflux and interactions. Pharm Res. 2013 Apr;30(4):996-1007. | ||||
| 11 | Impact of OATP transporters on pharmacokinetics. Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Oct;158(3):693-705. | ||||
| 12 | Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family in multidrug resistance: A review of the past decade. Cancer Lett. 2016 Jan 1;370(1):153-64. | ||||
| 13 | A comparison of the effects of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors on the CYP3A4-dependent oxidation of mexazolam in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos. 2001 Mar;29(3):282-8. | ||||
| 14 | Genetic polymorphisms in cytochrome P450 enzymes: effect on efficacy and tolerability of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2004;4(4):247-55. | ||||
| 15 | Pharmacogenomics of statins: understanding susceptibility to adverse effects. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2016 Oct 3;9:97-106. | ||||
| 16 | In vitro metabolism of simvastatin in humans [SBT]identification of metabolizing enzymes and effect of the drug on hepatic P450s. Drug Metab Dispos. 1997 Oct;25(10):1191-9. | ||||
| 17 | Drug interactions with lipid-lowering drugs: mechanisms and clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Dec;80(6):565-81. | ||||
| 18 | Simvastatin inactivates beta1-integrin and extracellular signal-related kinase signaling and inhibits cell proliferation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2007 Jun;98(6):890-9. | ||||
| 19 | Alternative splicing of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase is associated with plasma low-density lipoprotein cholesterol response to simvastatin. Circulation. 2008 Jul 22;118(4):355-62. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.773267. Epub 2008 Jun 16. | ||||
| 20 | Physiogenomic association of statin-related myalgia to serotonin receptors. Muscle Nerve. 2007 Sep;36(3):329-35. doi: 10.1002/mus.20871. | ||||
| 21 | Hydroxychloroquine decreases human MSC-derived osteoblast differentiation and mineralization in vitro. J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Feb;22(2):873-882. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13373. Epub 2017 Oct 3. | ||||
| 22 | Impaired migration of trophoblast cells caused by simvastatin is associated with decreased membrane IGF-I receptor, MMP2 activity and HSP27 expression. Hum Reprod. 2007 Apr;22(4):1161-7. doi: 10.1093/humrep/del464. Epub 2006 Dec 11. | ||||
| 23 | Suppression of RAGE as a basis of simvastatin-dependent plaque stabilization in type 2 diabetes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006 Dec;26(12):2716-23. | ||||
| 24 | In-vivo effects of simvastatin and rosuvastatin on global gene expression in peripheral blood leucocytes in a human inflammation model. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2008 Feb;18(2):109-20. | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 26 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 28 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Tibsovo (ivosidenib). Agios Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 30 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 31 | Holtzman CW, Wiggins BS, Spinler SA "Role of P-glycoprotein in statin drug interactions." Pharmacotherapy 26 (2006): 1601-7. [PMID: 17064205] | ||||
| 32 | Agbin NE, Brater DC, Hall SD "Interaction of diltiazem with lovastatin and pravastatin." Clin Pharmacol Ther 61 (1997): 201. [PMID: 9797793] | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 34 | Andreou ER, Ledger S "Potential drug interaction between simvastatin and danazol causing rhabdomyolysis." Can J Clin Pharmacol 10 (2003): 172-4. [PMID: 14712320] | ||||
| 35 | Ayanian JZ, Fuchs CS, Stone RM "Lovastatin and rhabdomyolysis." Ann Intern Med 109 (1988): 682-3. [PMID: 3421582] | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Ketek (telithromycin). Aventis Pharmaceuticals, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Balversa (erdafitinib). Janssen Products, LP, Horsham, PA. | ||||
| 38 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Talzenna (talazoparib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 40 | Alderman CP "Possible interaction between nefazodone and pravastatin." Ann Pharmacother 33 (1999): 871. [PMID: 10466919] | ||||
| 41 | Gaw A, Wosornu D "Simvastatin during warfarin therapy in hyperlipoproteinaemia." Lancet 340 (1992): 979-80. [PMID: 1357387] | ||||
| 42 | He K, Woolf TF, Hollenberg PF "Mechanism-based inactivation of cytochrome P-450-3A4 by mifepristone (RU486)." J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288 (1999): 791-7. [PMID: 9918590] | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Kalydeco (ivacaftor). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Trileptal (oxcarbazepine) Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 46 | EMEA. European Medicines Agency "EPARs. European Union Public Assessment Reports.". | ||||
| 47 | Akram K, Rao S, Parker M "A lesson for everyone in drug-drug interactions." Int J Cardiol 118 (2007): e19-20. [PMID: 17368833] | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Olysio (simeprevir). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 49 | Bogman K, Peyer AK, Torok M, Kusters E, Drewe J "HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and P-glycoprotein modulation." Br J Pharmacol 132 (2001): 1183-92. [PMID: 11250868] | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Priftin (rifapentine). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 51 | Product Information. Accolate (zafirlukast). Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 52 | Product Information. Rescriptor (delavirdine). Pharmacia and Upjohn, Kalamazoo, MI. | ||||
| 53 | Barry M, Mulcahy F, Merry C, Gibbons S, Back D "Pharmacokinetics and potential interactions amongst antiretroviral agents used to treat patients with HIV infection." Clin Pharmacokinet 36 (1999): 289-304. [PMID: 10320951] | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Rukobia (fostemsavir). ViiV Healthcare, Research Triangle Park, NC. | ||||
| 55 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 56 | Argov Z, Mastaglia FL "Drug-induced peripheral neuropathies." Br Med J 1 (1979): 663-6. [PMID: 219931] | ||||
| 57 | Product Information. Zocor (simvastatin). Merck & Co, Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 58 | Product Information. Zurampic (lesinurad). Astra-Zeneca Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 59 | Product Information. Alunbrig (brigatinib). Ariad Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 60 | Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF "Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: Culprit drugs, prevention and management." Drug Saf 42 (2019): 827-47. [PMID: 30888626] | ||||
| 61 | Product Information. Lorbrena (lorlatinib). Pfizer U.S. Pharmaceuticals Group, New York, NY. | ||||
| 62 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 63 | Product Information. Braftovi (encorafenib). Array BioPharma Inc., Boulder, CO. | ||||
| 64 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 65 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 66 | Product Information. Xenleta (lefamulin). Nabriva Therapeutics US, Inc., King of Prussia, PA. | ||||
| 67 | Product Information. Zokinvy (lonafarnib). Eiger BioPharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA. | ||||
| 68 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 69 | Product Information. ReVia (naltrexone). DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
| 70 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 71 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 72 | Barshes NR, Goodpastor SE, Goss JA "Sirolimus-atorvastatin drug interaction in the pancreatic islet transplant recipient." Transplantation 76 (2003): 1649-50. [PMID: 14702546] | ||||
| 73 | Product Information. Farxiga (dapagliflozin). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 74 | Chouhan UM, Chakrabarti S, Millward LJ "Simvastatin interaction with clarithromycin and amiodarone causing myositis." Ann Pharmacother 39 (2005): 1760-1. [PMID: 16159992] | ||||
