Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM7ICNU)
| Drug Name |
Doxycycline
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Atridox; Azudoxat; DOXY; Deoxymykoin; Dossiciclina; Doxiciclina; Doxitard; Doxivetin; Doxycen; Doxychel; Doxycin; Doxycyclin; Doxycyclinum; Doxysol; Doxytec; Doxytetracycline; Hydramycin; Investin; Jenacyclin; Liviatin; Monodox; Oracea; Ronaxan; Spanor; Supracyclin; Vibramycin; Vibramycine; Vibravenos; DOXCYCLINE ANHYDROUS; DOXYCYCLINE CALCIUM; DOXYCYCLINE MONOHYDRATE; Dossiciclina [DCIT]; Doxiciclina [Italian]; Doxycycline anhydrous; Doxycycline hyclate; Vibramycin Novum; Alpha-Doxycycline; Alti-Doxycycline; Apo-Doxy; BMY-28689; BU-3839T; Doxiciclina [INN-Spanish]; Doxy-Caps; Doxy-Puren; Doxy-Tabs; Doxychel (TN); Doxycycline (INN); Doxycycline (TN); Doxycycline (anhydrous); Doxycycline (internal use); Doxycycline-Chinoin; Doxycyclinum [INN-Latin]; Novo-Doxylin; Nu-Doxycycline; Periostat (TN); Vibra-tabs; Alpha-6-Deoxyoxytetracycline; DMSC (*Fosfatex); Doxycycline (200mg/day) or Placebo; Monodox (*monohydrate); Vibramycin (*monohydrate); Vivox (*Hyclate); GS-3065 (*monohydrate); Alpha-6-Deoxy-5-hydroxytetracycline; (2E,4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6R,12aS)-2-[amino(hydroxy)methylidene]-4-(dimethylamino)-5,10,11,12a-tetrahydroxy-6-methyl-4a,5,5a,6-tetrahydro-4H-tetracene-1,3,12-trione; (2Z)-2-[amino(hydroxy)methylidene]-4-(dimethylamino)-5,10,11,12a-tetrahydroxy-6-methyl-4a,5,5a,6-tetrahydro-4H-tetracene-1,3,12-trione; (2Z,4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6R)-2-[amino(hydroxy)methylidene]-4-(dimethylamino)-5,10,11,12a-tetrahydroxy-6-methyl-4a,5,5a,6-tetrahydro-4H-tetracene-1,3,12-trione; (2Z,4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6R,12aS)-2-[amino(hydroxy)methylidene]-4-(dimethylamino)-5,10,11,12a-tetrahydroxy-6-methyl-4a,5,5a,6-tetrahydro-4H-tetracene-1,3,12-trione; (4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6R,12aS)-4-(dimethylamino)-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide; 2-Naphthacenecarboxamide, 4-(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-, (4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6R,12aS); 5-Hydroxy-alpha-6-deoxytetracycline; 6-Deoxyoxytetracycline; 6-Deoxytetracycline; 6-alpha-Deoxy-5-oxytetracycline; 6alpha-Deoxy-5-oxytetracycline
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiinflammatory Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Gram negative and gram positive bacteriaVarious aerobic and anaerobic microorganismsPlasmodium falciparum
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
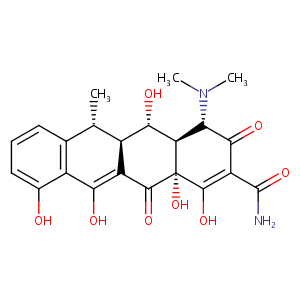 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 444.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -0.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Doxycycline (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Doxycycline FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6464). | ||||
| 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00764361) Safety Study of Topical Doxycycline Gel for Adult Diabetic Lower Extremity Ulcers. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 8 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 9 | Mammalian drug efflux transporters of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) family in multidrug resistance: A review of the past decade. Cancer Lett. 2016 Jan 1;370(1):153-64. | ||||
| 10 | A further interaction study of quinine with clinically important drugs by human liver microsomes: determinations of inhibition constant (Ki) and type of inhibition. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1999 Jul-Sep;24(3):272-8. | ||||
| 11 | Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of targeted tetracycline derivatives: effects on inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007 Mar 15;15(6):2368-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.01.026. Epub 2007 Jan 19. | ||||
| 12 | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor protects lung adenocarcinoma cells against cigarette sidestream smoke particulates-induced oxidative stress. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Mar 15;259(3):293-301. | ||||
| 13 | Functional and histochemical analysis of MDR3 P-glycoprotein in a tetracycline-controlled gene expression system. Eur J Med Res. 2000 Dec 29;5(12):517-22. | ||||
| 14 | Chloramphenicol causes mitochondrial stress, decreases ATP biosynthesis, induces matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression, and solid-tumor cell invasion. Toxicol Sci. 2010 Jul;116(1):140-50. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq085. Epub 2010 Mar 25. | ||||
| 15 | Systems pharmacological analysis of drugs inducing stevens-johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Chem Res Toxicol. 2015 May 18;28(5):927-34. doi: 10.1021/tx5005248. Epub 2015 Apr 3. | ||||
| 16 | A high-content screen identifies novel compounds that inhibit stress-induced TDP-43 cellular aggregation and associated cytotoxicity. J Biomol Screen. 2014 Jan;19(1):44-56. doi: 10.1177/1087057113501553. Epub 2013 Sep 9. | ||||
| 17 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 18 | Elliott GR "Sodium bicarbonate and oral tetracycline." Clin Pharmacol Ther 13 (1972): 459. [PMID: 5026384] | ||||
| 19 | Gardner K, Cox T, Digre KB "Idiopathic intracranial hypertension associated with tetracycline use in fraternal twins: case reports and review." Neurology 45 (1995): 6-10. [PMID: 7824136] | ||||
| 20 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Canadian Product Information.". | ||||
| 21 | Covington TR, Lawson LC, Young LL, eds. "Handbook of Nonprescription Drugs. 10th ed." Washington, DC: American Pharmaceutical Association (1993):. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 23 | Neuvonen PJ, Penttila O "Interaction between doxycycline and barbiturates." Br Med J 1 (1974): 535-6. [PMID: 4817187] | ||||
| 24 | Gotz VP, Ryerson GG "Evaluation of tetracycline on theophylline disposition in patients with chronic obstructive airways disease." Drug Intell Clin Pharm 20 (1986): 694-6. [PMID: 3757782] | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 26 | Friedman CI, Huneke AL, Kim MH, Powell J "The effect of ampicillin on oral contraceptive effectiveness." Obstet Gynecol 55 (1980): 33-7. [PMID: 7188714] | ||||
| 27 | Multum Information Services, Inc. Expert Review Panel. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil). Roche Laboratories, Nutley, NJ. | ||||
| 29 | Neuvonen PJ, Penttila O, Lehtovaara R, Aho K "Effect of antiepileptic drugs on the elimination of various tetracycline derivatives." Eur J Clin Pharmacol 9 (1975): 147-54. [PMID: 1233262] | ||||
| 30 | Lindenbaum J, Rund DG, Butler VP Jr, Tse-Eng D, Saha JR "Inactivation of digoxin by the gut flora: reversal by antibiotic therapy." N Engl J Med 305 (1981): 789-94. [PMID: 7266632] | ||||
| 31 | Colmenero JD, Fernandezgallardo LC, Agundez JAG, Sedeno J, Benitez J, Valverde E "Possible implications of doxycycline-rifampin interaction for treatment of brucellosis." Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38 (1994): 2798-802. [PMID: 7695265] | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 34 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 35 | Campbell NR, Hasinoff BB "Iron supplements: a common cause of drug interactions." Br J Clin Pharmacol 31 (1991): 251-5. [PMID: 2054263] | ||||
| 36 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 37 | Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF "Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: Culprit drugs, prevention and management." Drug Saf 42 (2019): 827-47. [PMID: 30888626] | ||||
| 38 | Zhao XJ, Ishizaki T "A further interaction study of quinine with clinically important drugs by human liver microsomes: determinations of inhibition constant (K-i) and type of inhibition." Eur J Drug Metab Pharm 24 (1999): 272-8. [PMID: 10716067] | ||||
| 39 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 41 | Albert KS, Welch RD, DeSante KA, DiSanto AR "Decreased tetracycline bioavailability caused by a bismuth subsalicylate antidiarrheal mixture." J Pharm Sci 68 (1979): 586-8. [PMID: 435335] | ||||
