Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMQCTIH)
| Drug Name |
Digoxin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
digoxin; 20830-75-5; 12beta-Hydroxydigitoxin; Digoxine; Lanoxin; Lanoxicaps; Digossina; Digoxina; Digoxinum; Digosin; Lanicor; Digacin; Dilanacin; CHEBI:4551; MLS000069819; Lanacordin; Cardiogoxin; Eudigox; Davoxin; SMR000059217; Rougoxin; Mapluxin; Lenoxin; Lanacrist; Dynamos; Vanoxin; Neo-Lanicor; Lanoxin PG; Digoxin Pediatric; Digoxin Nativelle; SK-Digoxin; UNII-73K4184T59; Homolle's digitalin; Hemigoxine Nativelle; MFCD00003674; Digitek (TN); Lanoxicaps (TN); Lanoxin (TN); Digoxin (JP15/USP); (3beta,5beta,12beta)-3-{[2,6-dideoxy-beta-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1->4)-2,6-dideoxy-beta-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl-(1->4)-2,6-dideoxy-beta-D-ribo-hexopyranosyl]oxy}-12,14-dihydroxycard-20(22)-enolide; 4-[(1S,2S,5S,7R,10R,11S,14R,15S,16R)-5-{[(2R,4S,5S,6R)-5-{[(2S,4S,5S,6R)-5-{[(2S,4S,5S,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-11,16-dihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8700^{2,7}; [3H]digoxin
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antiarrhythmic Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
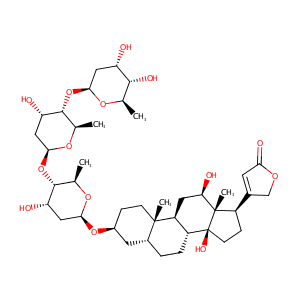 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 3 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 780.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Digoxin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Digoxin (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4726). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Digoxin FDA Label | ||||
| 3 | Iisalo E: Clinical pharmacokinetics of digoxin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1977 Jan-Feb;2(1):1-16. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197702010-00001. | ||||
| 4 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 5 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 6 | FDA Approved Drug Products: Lanoxin (digoxin) oral tablets | ||||
| 7 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 8 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 9 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1227). | ||||
| 10 | Fab antibody fragments: some applications in clinical toxicology. Drug Saf. 2004;27(14):1115-33. | ||||
| 11 | MDR3 P-glycoprotein, a phosphatidylcholine translocase, transports several cytotoxic drugs and directly interacts with drugs as judged by interference with nucleotide trapping. J Biol Chem. 2000 Aug 4;275(31):23530-9. | ||||
| 12 | Functional complementation between a novel mammalian polygenic transport complex and an evolutionarily ancient organic solute transporter, OSTalpha-OSTbeta. J Biol Chem. 2003 Jul 25;278(30):27473-82. | ||||
| 13 | Isolation and characterization of a digoxin transporter and its rat homologue expressed in the kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Mar 9;101(10):3569-74. | ||||
| 14 | Drug Interactions in Infectious Diseases. | ||||
| 15 | Organic anion-transporting polypeptide B (OATP-B) and its functional comparison with three other OATPs of human liver. Gastroenterology. 2001 Feb;120(2):525-33. | ||||
| 16 | MDR1 function is sensitive to the phosphorylation state of myosin regulatory light chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Jul 16;398(1):7-12. | ||||
| 17 | Omeprazole-associated digoxin toxicity. South Med J. 2007 Apr;100(4):400-2. | ||||
| 18 | Mechanistic insight into digoxin inactivation by Eggerthella lenta augments our understanding of its pharmacokinetics. Gut Microbes. 2014 Mar-Apr;5(2):233-8. | ||||
| 19 | Digoxin and ouabain induce P-glycoprotein by activating calmodulin kinase II and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in human colon cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009 Nov 1;240(3):385-92. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.07.026. Epub 2009 Jul 30. | ||||
| 20 | Human breast cancer resistance protein: interactions with steroid drugs, hormones, the dietary carcinogen 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo(4,5-b)pyridine, and transport of cimetidine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Jan;312(1):144-52. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.073916. Epub 2004 Sep 13. | ||||
| 21 | Cell-based and cytokine-directed chemical screen to identify potential anti-multiple myeloma agents. Leuk Res. 2010 Jul;34(7):917-24. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2009.12.002. Epub 2010 Feb 8. | ||||
| 22 | Insulin interacts directly with Na?/K?ATPase and protects from digoxin toxicity. Toxicology. 2012 Sep 4;299(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.04.013. Epub 2012 May 4. | ||||
| 23 | Brown DD, Dormois JC, Abraham GN, et al "Effect of furosemide on the renal excretion of digoxin." Clin Pharmacol Ther 20 (1976): 395-400. [PMID: 975715] | ||||
| 24 | Allen MD, Greenblatt DJ, Harmatz JS, Smith TW "Effect of magnesium--aluminum hydroxide and kaolin--pectin on absorption of digoxin from tablets and capsules." J Clin Pharmacol 21 (1981): 26-30. [PMID: 7012189] | ||||
| 25 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 26 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 27 | Binnion PF, McDermott M, LeSher D "Bioavailability of digoxin." Lancet 1 (1973): 1118. [PMID: 4122032] | ||||
| 28 | Lindenbaum J, Maulitz RM, Butler VP "Inhibition of digoxin absorption by neomycin." Gastroenterology 71 (1976): 399-404. [PMID: 950089] | ||||
| 29 | Belz GG, Aust PE, Munkes R "Digoxin plasma concentrations and nifedipine ." Lancet 1 (1981): 844-5. [PMID: 6111709] | ||||
| 30 | Ochs HR, Greenblatt DJ, Verburg-Ochs B "Effect of alprazolam on digoxin kinetics and creatinine clearance." Clin Pharmacol Ther 38 (1985): 595-8. [PMID: 2865030] | ||||
| 31 | Castillo-Ferrando JR, Garcia M, Carmona J "Digoxin levels and diazepam." Lancet 2 (1980): 368. [PMID: 6105500] | ||||
| 32 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 33 | Andersson T "Omeprazole drug interaction studies." Clin Pharmacokinet 21 (1991): 195-212. [PMID: 1764870] | ||||
| 34 | Lindenbaum J, Rund DG, Butler VP Jr, Tse-Eng D, Saha JR "Inactivation of digoxin by the gut flora: reversal by antibiotic therapy." N Engl J Med 305 (1981): 789-94. [PMID: 7266632] | ||||
| 35 | Hughes J, Crowe A. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux of digoxin and its metabolites by macrolide antibiotics.?J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;113(4):315-324. [PMID: 20724802] | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Balversa (erdafitinib). Janssen Products, LP, Horsham, PA. | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Tukysa (tucatinib). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 38 | Boyd RA, Stern RH, Stewart BH, et al. "Atorvastatin coadministration may increase digoxin concentrations by inhibition of intestinal P-glycoprotein-mediated secretion." J Clin Pharmacol 40 (2000): 91-8. [PMID: 10631627] | ||||
| 39 | Storstein L, Janssen H "Studies on digitalis VI: the effect of heparin on serum protein binding of digitoxin and digoxin." Clin Pharmacol Ther 20 (1976): 15-23. [PMID: 1277722] | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Korlym (mifepristone). Corcept Therapeutics Incorporated, Menlo Park, CA. | ||||
| 41 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 42 | Product Information. Kalydeco (ivacaftor). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 43 | Semple P, Tilstone WJ, Lawson DH "Furosemide and urinary digoxin clearance." N Engl J Med 293 (1975): 612-3. [PMID: 902451] | ||||
| 44 | Alderman CP, Allcroft PD "Digoxin-itraconazole interaction: possible mechanisms." Ann Pharmacother 31 (1997): 438-40. [PMID: 9101006] | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Colcrys (colchicine). AR Scientific Inc, Philadelphia, PA. | ||||
| 46 | Becquemont L, Verstuyft C, Kerb R, et al. "Effect of grapefruit juice on digoxin pharmacokinetics in humans." Clin Pharmacol Ther 70 (2001): 311-6. [PMID: 11673746] | ||||
| 47 | Bjornsson TD, Huang AT, Roth P, Jacob DS, Christenson R "Effects of high-dose cancer chemotherapy on the absorption of digoxin in two different formulations." Clin Pharmacol Ther 39 (1986): 25-8. [PMID: 3943266] | ||||
| 48 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 49 | Frye RL, Braunwald E "Studies on digitalis. III: The influence of triiodothyronine on digitalis requirements." Circulation 23 (1961): 376-82. [PMID: 13702336] | ||||
| 50 | Product Information. Belsomra (suvorexant). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 51 | Product Information. Tabrecta (capmatinib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 52 | Brater DC, Morrelli HF "Systemic alkalosis and digitalis related arrhythmias." Acta Med Scand Suppl 647 (1981): 79-85. [PMID: 6942644] | ||||
| 53 | Product Information. Gilenya (fingolimod). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 54 | Product Information. Zeposia (ozanimod). Celgene Corporation, Summit, NJ. | ||||
| 55 | Product Information. Varubi (rolapitant). Tesaro Inc., Waltham, MA. | ||||
| 56 | Fraser EJ, Leach RH, Poston JW, Bold AM, Culank LS, Lipede AB "Dissolution-rates and bioavailability of digoxin tablets." Lancet 1 (1973): 1393. [PMID: 4122785] | ||||
| 57 | Product Information. Zokinvy (lonafarnib). Eiger BioPharmaceuticals, Palo Alto, CA. | ||||
| 58 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 59 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 60 | EMEA. European Medicines Agency "EPARs. European Union Public Assessment Reports.". | ||||
| 61 | Product Information. Victoza (liraglutide). Novo Nordisk Pharmaceuticals Inc, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 62 | Bajaj BP, Baig MW, Perrins EJ "Amiodarone-induced torsades de pointes: the possible facilitatory role of digoxin." Int J Cardiol 33 (1991): 335-7. [PMID: 1743800] | ||||
