Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM5FSJA)
| Drug Name |
Glimepiride
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Amarel; Amaryl; Endial; Glimepirid; Glimepirida; Glimepiridum; Glimepride; Glimer; Glymepirid; Roname; Solosa; Glimepirida [Spanish]; Glimepiridum [Latin]; Sandoz glimepiride; HOE 490; Amaryl (TN); Hoe-490; Novo-glimepiride; PMS-glimepiride; Ratio-glimepiride; Amaryl, Glista OD, Glimepiride; Glimepiride [USAN:BAN:INN]; Glimepiride (JAN/USP/INN); 1-((p-(2-(3-Ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-3-pyrroline-1-carboxamido)ethyl)phenyl)sulfonyl)-3-(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)urea; 1-{[4-(2-{[(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-1-yl)carbonyl]amino}ethyl)phenyl]sulfonyl}-3-(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)urea; 3-ethyl-4-methyl-N-[2-(4-{[(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoyl]sulfamoyl}phenyl)ethyl]-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxamide; 3-ethyl-4-methyl-n-(4-(n-((1r,4r)-4-methylcyclohexylcarbamoyl)sulfamoyl)phenethyl)-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro; 4-ethyl-3-methyl-N-[2-[4-[(4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoylsulfamoyl]phenyl]ethyl]-5-oxo-2H-pyrrole-1-carboxamide; 64598P
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Hypoglycemic Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
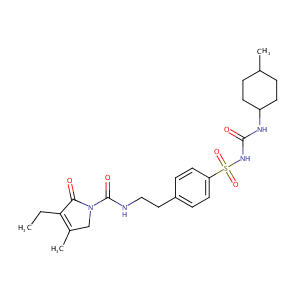 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 490.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 3.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug Transporter (DTP) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Expression Atlas of This Drug
| The Studied Disease | Diabetic complication | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICD Disease Classification | 5A2Y | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Expression Atlas (MEA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Glimepiride
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Glimepiride (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6820). | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Basit A, Riaz M, Fawwad A: Glimepiride: evidence-based facts, trends, and observations (GIFTS). [corrected]. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2012;8:463-72. doi: 10.2147/HIV.S33194. Epub 2012 Aug 15. | ||||
| 3 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 4 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 5 | Amaryl (glimepiride) Product Monograph - Sanofi in Canada | ||||
| 6 | AMARYL (glimepiride) FDA Label | ||||
| 7 | Sulfonylureas and their use in clinical practice. Arch Med Sci. 2015 Aug 12;11(4):840-8. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2015.53304. Epub 2015 Aug 11. | ||||
| 8 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 9 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 10 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 11 | Mechanism of disopyramide-induced hypoglycaemia in a patient with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2009 Jan;26(1):76-8. | ||||
| 12 | Early identification of clinically relevant drug interactions with the human bile salt export pump (BSEP/ABCB11). Toxicol Sci. 2013 Dec;136(2):328-43. | ||||
| 13 | Effect of CYP2C9 genetic polymorphisms on the efficacy and pharmacokinetics of glimepiride in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006 May;72(2):148-54. | ||||
| 14 | Initro inhibition of AKR1Cs by sulphonylureas and the structural basis. Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Oct 5;240:310-5. | ||||
| 15 | Interference with bile salt export pump function is a susceptibility factor for human liver injury in drug development. Toxicol Sci. 2010 Dec; 118(2):485-500. | ||||
| 16 | A potential role of calpains in sulfonylureas (SUs) -mediated death of human pancreatic cancer cells (1.2B4). Toxicol In Vitro. 2021 Jun;73:105128. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2021.105128. Epub 2021 Feb 27. | ||||
| 17 | Product Information. Starlix (nateglinide) Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 18 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 19 | Abad S, Moachon L, Blanche P, Bavoux F, Sicard D, Salmon-Ceron D "Possible interaction between glicazide, fluconazole and sulfamethoxazole resulting in severe hypoglycaemia." Br J Clin Pharmacol 52 (2001): 456-7. [PMID: 11678792] | ||||
| 20 | Bussing R, Gende A "Severe hypoglycemia from clarithromycin-sulfonylurea drug interaction." Diabetes Care 25 (2002): 1659-61. [PMID: 12196446] | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Amaryl (glimepiride). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Alinia (nitazoxanide). Romark Laboratories L.C., Tampa, FL. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 24 | Product Information. Korlym (mifepristone). Corcept Therapeutics Incorporated, Menlo Park, CA. | ||||
| 25 | Kvinssland S, Lonning PE, Ueland PM "Aminoglutethimide as an inducer of microsomal enzymes. Part 1: Pharmacological aspects." Breast Cancer Res Treat 7 (1986): s73-6. [PMID: 2943339] | ||||
| 26 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Canadian Product Information.". | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Kalydeco (ivacaftor). Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Prevymis (letermovir). Merck & Company Inc, Whitehouse Station, NJ. | ||||
| 29 | Product Information. Emend (aprepitant). Merck & Company Inc, West Point, PA. | ||||
| 30 | Humphries TJ "Clinical implications of drug interactions with the cytochrome P-450 enzyme system associated with omeprazole." Dig Dis Sci 36 (1991): 1665-9. [PMID: 1748033] | ||||
| 31 | Dey NG, Castleden CM, Ward J, et al "The effect of cimetidine on tolbutamide kinetics." Br J Clin Pharmacol 16 (1983): 438-40. [PMID: 6626438] | ||||
| 32 | Borcherding SM, Baciewicz AM, Self TH "Update on rifampin drug interactions." Arch Intern Med 152 (1992): 711-6. [PMID: 1558427] | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Priftin (rifapentine). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 34 | Product Information. Intelence (etravirine). Ortho Biotech Inc, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 35 | Gachalyi B, Tornyossy, Vas A, Kaldor A "Effect of alphamethyldopa on the half-lives of antipyrine, tolbutamide and D-glucaric acid excretion in man." Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 18 (1980): 133-5. [PMID: 6103880] | ||||
| 36 | Christensen LK, Hansen JM, Kristensen M "Sulphaphenazole-induced hypoglycemic attacks in tolbutamide-treated diabetics." Lancet 2 (1963): 1298-301. [PMID: 14071924] | ||||
| 37 | Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF "Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: Culprit drugs, prevention and management." Drug Saf 42 (2019): 827-47. [PMID: 30888626] | ||||
| 38 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 39 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 40 | Product Information. Gleevec (imatinib mesylate). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 41 | EMA. European Medicines Agency. European Union "EMA - List of medicines under additional monitoring.". | ||||
| 42 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 43 | Product Information. Tracleer (bosentan). Acetelion Pharmaceuticals US, Inc, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
| 44 | Product Information. Arava (leflunomide). Hoechst Marion-Roussel Inc, Kansas City, MO. | ||||
| 45 | Product Information. Plavix (clopidogrel). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
